Cornell scientists link E. coli bacteria to Crohn's disease
Advertisement
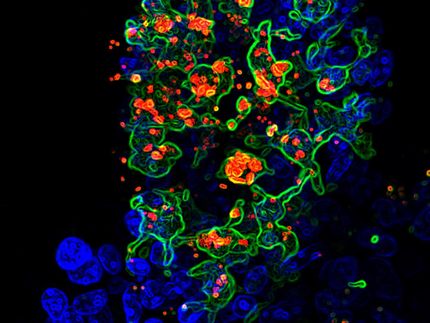
A team of Cornell scientists has discovered that intestinal inflammation in patients with Crohn's disease may be associated with a novel group of E. coli bacteria with genes similar to bacteria that cause diseases ranging from salmonella to cholera and even bubonic plague.
The team - which includes scientists from Cornell's College of Veterinary Medicine, College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, and Weill Cornell Medical College - published the findings in Multidisciplinary Journal of Microbial Ecology.
Mycobacterium avium paratuberculosis (MAP) bacteria have long been suspected to play a pivotal role in the development of Crohn's disease, but the mechanisms that drive the inflammatory response have remained elusive.
The researchers compared the intestines of healthy individuals with the intestines of patients with Crohn's restricted to the ileum and the colon. They found an increased level of E. coli in more inflamed areas of the small intestines instead of MAP bacteria.
"Our findings raise the possibility that a novel group of E. coli contains opportunistic pathogens that may be causally related to chronic intestinal inflammation in susceptible individuals," said Kenneth Simpson, professor of small animal medicine at the College of Veterinary Medicine and the paper's senior author. "They suggest that an integrated approach that considers an individual's mucosa-associated flora in addition to disease phenotype and genotype may improve outcome," he said.
Most read news
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.