Biocatalysts are a bridge to greener, more powerful chemistry
Advertisement
New research from the University of Michigan Life Sciences Institute is building a bridge from nature's chemistry to greener, more efficient synthetic chemistry.
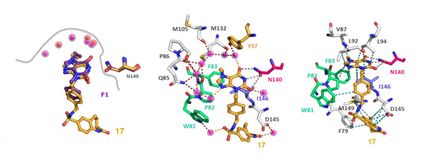
Researchers in the lab of Alison Narayan analyzed biocatalysts evolved by nature for their effectiveness in a variety of synthetic chemical reactions. The results open the door to promising practices for chemists, pointing to not only more efficient but more powerful tools for chemists.
The researchers started with microorganisms that have, over the millennia, developed complex chemical reactions to create molecules with important biological activity for various purposes, such as defense mechanisms. The scientists then analyzed the chemical pathways that give rise to these potentially useful molecules to determine how they can be repurposed to create compounds synthetically in the lab.
"Nature has evolved catalytic tools that would enable chemists to build molecules that we can't easily build just using traditional chemistry," said Narayan, the senior study author and assistant professor at the LSI, where her lab is located. "Our work bridges the two worlds of biosynthesis and synthetic chemistry."
To build complex, bioactive molecules -- like the molecules that allow drugs to find the right biological targets in our bodies -- synthetic chemists often use a process called oxidative dearomatization. This process converts flat molecules into three-dimensional structures that are more reactive. But traditional oxidative dearomatization methods have several flaws.
Because they require the use of a chemical reagent to convert the starting material into the desired end product, the reactions themselves are fairly wasteful. In addition, the reagents demonstrate poor selectivity in the transformation, resulting in a mixture of compounds that contains several unnecessary, and sometimes harmful, variants of the desired product molecule.
"It's not a very efficient process," said Narayan, who is also an assistant professor of chemistry in the U-M College of Literature, Science, and the Arts. "You can end up with various structures when you really want only this one specific structure--and you generate a lot of waste in the process."
In this recent study, the Narayan lab demonstrated that enzyme catalysts have the potential to solve these issues.
Enzymes are efficient catalysts, generating many product molecules from a single molecule of the catalyst, leading to less waste. And Narayan's lab found that the catalysts perform the reactions with improved selectivity--meaning that the reactions produce only the desired molecular structure.
These enzymes have not yet been widely adopted by chemists because their overall utility and robustness for chemistry have not been demonstrated, Narayan said.
"The work being done in the field of biosynthesis primarily focuses on understanding how molecules are made in nature and identifying the single reaction an enzyme does in its natural context," she said. "We have to figure out how an enzyme is useful in the field of synthetic chemistry--what can it do, what types of molecules it works with--so that chemists can just go to the literature and see how they can use this tool."
Narayan's research program begins to close the gap between these two fields by testing enzymes not just for their natural roles, but for the roles they could play in a variety of reactions. The lab also has developed methods to make these enzymes easy to handle in bulk and share with other chemists.
"We're showing that these enzymes can do more than the one specific task they evolved to do in nature," said graduate student Summer Baker Dockrey, the lead study author. "They can be surprisingly generalizable and could prove to be highly selective tools."
The lab is now working on engineering these enzymes to perform more reactions.
"We are really starting to build the library of new, efficient, powerful tools for chemists," Narayan said.