A new twist on asymmetric catalysis
Advertisement
In the same way a glove will only fit one hand, molecules have the symmetry that controls their behavior and interactions. In drug design, this means reversing the symmetry of a molecule can mean the difference between an effective treatment or a compound that has serious negative effects. As a further complication, making chemicals as a single pure mirror image, or separating mixtures of the two types, is very difficult.
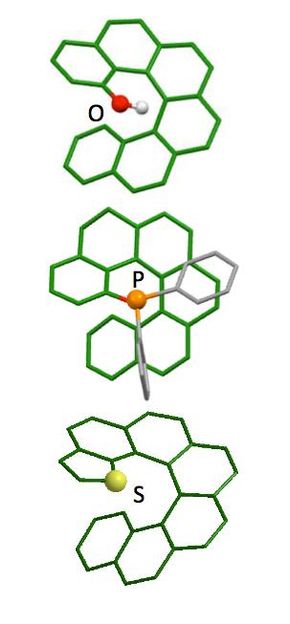
This is the structure of functional helicene.
Osaka University
Now a team of chemists of Osaka and Iwate Medical University has now developed a highly efficient way to make a unique screw-like chemical that could offer new routes to pure mirror images of other molecules.
"The twisted shape of helicenes makes them ideal for use in asymmetric catalysis" lead author Tetsuya Tsujihara says. "We previously developed a simple synthesis and resolution for this class of molecule and now, for the first time, we have added a thiophene group."
Helicene is a molecule with six hexagonal benzene molecules fused together so the rings twist back over themselves out of the plane of the molecule. The direction of the twist is locked, meaning two possible helices are possible, each a mirror image of the other. Think of the way a screw might turn clockwise or anticlockwise depending on the direction of the thread.
The researchers built upon their earlier studies, making and separating the two mirror images of helicene molecules. This time they changed their structure to include a new sulfur-containing group. This change could allow the screw-shaped molecules to be used as asymmetric catalysts for controlling interactions of other chemicals in reactions to directly produce molecules of a single mirror image.
"Adding the thiophene group is new development of the helicene skeleton, which should change the physical properties of the molecule and make these much more interesting to materials scientists," coauthor Tomikazu Kawano says. "We are also continuing to explore the promising asymmetric reactivity of these twisted catalysts."























































