Born to break
Mutation causes fragile bones
Advertisement
Fragile bones are usually an old person's affliction, but sometimes children are born with them. Now, a team of researchers led by UConn professor Ernesto Canalis has shown in mice that a specific gene can cause the disease, called Hajdu-Cheney syndrome. Overabundant bone-absorbing cells may be causing the disorder's characteristic bone loss, and the researchers hope to find a potential treatment.
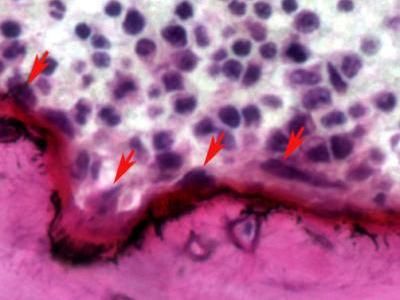
The picture shows a cross-section of the femur of a mouse. The white and purple cells are bone marrow, the pink area is bone, and the arrows show osteoclasts resorbing bone. This mouse has too many osteoclasts; it has a variant of the NOTCH2 gene that causes a disease akin to Hajdu-Cheney syndrome in humans.
Stefano Zanotti/Canalis Lab, UConn Health
People born with Hajdu-Cheney syndrome develop misshapen skeletons and bones that quickly start to soften and fracture. Researchers knew Hajdu-Cheney was an inherited disease, but they weren't sure which genetic mutation caused it. They suspected it was in a gene called NOTCH2, which has a specific mutation that appears in people with the syndrome. But Hajdu-Cheney is very rare, and it might just have been a coincidence that families with Hajdu-Cheney also happen to carry an unusual variant of NOTCH2.
To figure out whether the NOTCH2 variant really was responsible, Canalis and his colleagues replicated it in mice. The result was essentially a mouse version of Hajdu-Cheney syndrome.
"Until now, nobody understood why people afflicted with the disease had osteoporosis and fractures," says Canalis, a professor of orthopaedic surgery at UConn Health. His mice seem to provide the answers. They generate a larger pool of osteoclasts, cells that break down and resorb old bone. These cells also mature faster than they do in normal mice. So Hajdu-Cheney mice have far too much bone resorbed by their bodies, and new bone doesn't grow fast enough to replace it. This leads to mice with fragile bones, very similar to people with the disease.
There are a few symptoms of the disease in humans - such as shortened fingers and oddly shaped skull bones - that the mice don't display. But overall, the mouse model is a very good model of the human disease, Canalis says.
Knowing how the disease works also suggests how it may be treated. If people with Hajdu-Cheney have too many bone-resorbing cells, then it may help to suppress the formation or activity of those cells. And Canalis says scientists know how to do that. His group is currently working on treatments in mice.
Hajdu-Cheney is an incredibly rare disease, with fewer than 100 cases ever described. But there are good scientific reasons to study it. It can illuminate the workings of bone formation and destruction, and give insight into a gene important to both the skeleton and the immune system. It could also possibly tell us about Alagille syndrome, another, much more common genetic disease associated with NOTCH2. But for Canalis, even if Hajdu-Cheney only affects a few people from a few families, what causes such suffering and how to abate it is worth searching for.


























































