From bacteria and plants to novel anti-parasite therapies
Research insight to Nobel laureates Cambell and Omura
Advertisement
After decades of limited progress in developing durable therapies for parasitic diseases, the discoveries by this year’s Laureates radically changed the situation.
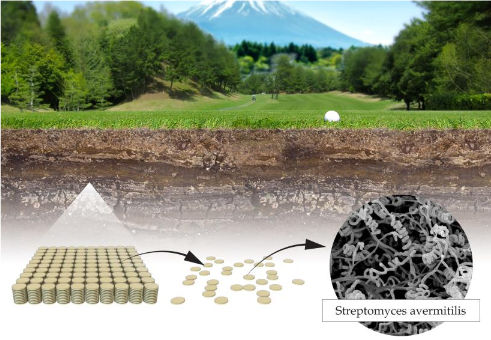
Satoshi Ōmura searched for novel strains of Streptomyces bacteria as a source for new bioactive compounds. He isolated microbes from soil samples in Japan, cultured them in the laboratory (inset to left) and characterized many thousands of Streptomyces cultures. From those, he selected around 50 cultures that appeared most promising, and one of these cultures later turned out to be Streptomyces avermitilis (inset to right), the source of Avermectin.
Nobel Foundation
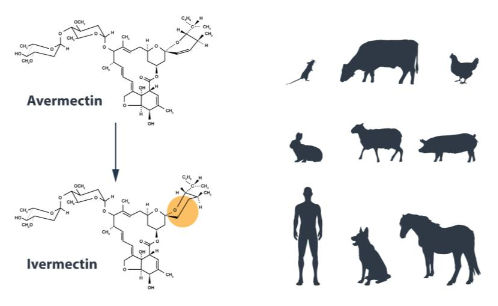
William C. Campbell discovered that one of Ōmura’s Streptomyces cultures was very effective in killing off parasites and the active compound, Avermectin, was purified. Avermectin was further modified to Ivermectin, which turned out to be highly effective in both animals and humans against a variety of parasites, including those that cause River Blindness and Lymphatic Filariasis.
Nobel Foundation
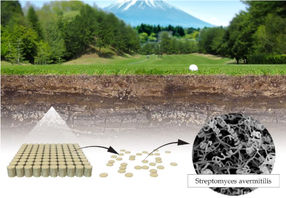
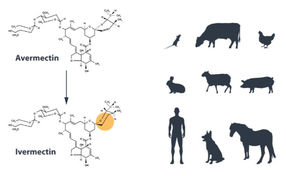
Satoshi Ōmura, a Japanese microbiologist and expert in isolating natural products, focused on a group of bacteria, Streptomyces, which lives in the soil and was known to produce a plethora of agents with antibacterial activities (including Streptomycin discovered by Selman Waksman, Nobel Prize 1952). Equipped with extraordinary skills in developing unique methods for large-scale culturing and characterization of these bacteria, Ōmura isolated new strains of Streptomyces from soil samples and successfully cultured them in the laboratory. From many thousand different cultures, he selected about 50 of the most promising, with the intent that they would be further analyzed for their activity against harmful microorganisms.
William C. Campbell, an expert in parasite biology working in the USA, acquired Ōmura’s Streptomyces cultures and explored their efficacy. Campbell showed that a component from one of the cultures was remarkably efficient against parasites in domestic and farm animals. The bioactive agent was purified and named Avermectin, which was subsequently chemically modified to a more effective compound called Ivermectin. Ivermectin was later tested in humans with parasitic infections and effectively killed parasite larvae (microfilaria). Collectively, Ōmura and Campbell’s contributions led to the discovery of a new class of drugs with extraordinary efficacy against parasitic diseases.



























































