Bioelectronics: Invention of the pH imaging microscope for applications including treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
Advertisement
The pH image sensor was invented by Kazuaki Sawada of Toyohashi University of Technology (Toyohashi Tech). The device enables two dimensional and simultaneous visualization of the pH and optical imaging of chemical activity of solutions and cell activity. Sawada and his group are looking for industrial partners for the development of other applications of the pH image sensor.
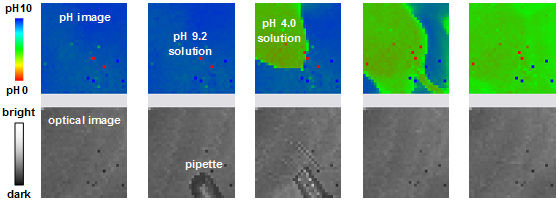
The pH and optical images from the pH image sensor

pH image sensor system

The CMOS device consists of an array of CCDs covered with functionalized membrane. Changes in the concentration and two dimensional distribution of hydrogen ions are detected by charge accumulation. In addition to monitoring the pH distribution, the device also yields optical images of the test sample.
The sensitivity of the pH imaging sensor is 100 times greater than ISFET devices and enables the determination of pH differences of 0.0001 pH. "High sensitivity is possible because we accumulate charge over well-defined periods of time," says Sawada. "The charge transfer is repeated many times, which gives huge improvements in signal to noise ratio."
The current pH image sensors consist of 128 x128 pixels, each with a sensing area of 10 x25 micrometers. Sawada and his group are developing pH image sensors with one million pixels, with each pixel being 10 x10 micrometers. "I have also launched a pH imaging consortium to address issues related to ion image sensing,” says Sawada. “In the future plans include pH imaging devices for visualizing the movement and distribution of other ions including as calcium and sodium."
Sawada's group has recently reported on the use of the sensor for real time imaging of acetylcholine (ACh) enzyme reactions. “We imaged changes in the distribution of Ach when nerve cells are stimulated with KCL,” says Sawada. “Insights in the variation of the concentration of ACh may lead to new methods for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.”