Gene increases effectiveness of drugs used to fight cancer and allows reduction in dosage
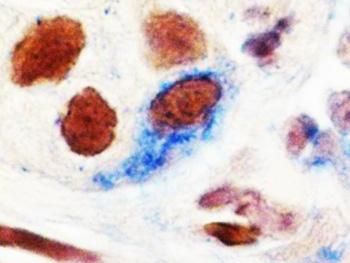
Researchers at the University of Granada have found a suicide gene, called 'gene E', which leads to the death of tumour cells derived from breast, lung and colon cancer, and prevents their growth. The importance of this new gene is that its use to fight cancer can reduce the potent drugs that are currently used, so that could mean more effective treatment for cancer.
This research was conducted by Ana Rosa Rama Ballesteros, from the Department of Anatomy and Human Embryology at the University of Granada , and directed by professors Antonia Aránega Jimenez, José Carlos Prados Salazar and Consolación Melguizo Alonso. Its aim was to study the possibility of reducing the dosage of drugs currently administered to cancer patients using combination therapy with suicide gene E.
Scientists from the UGR have shown that the bacteriophage phiX174 killer gene called E, can be used to induce death in tumour cells. So far, attempts to use many chemotherapeutic (cytotoxic) agents similar to the E gene have shown severe limitations resulting from their toxicity and their poor affinity with the tumour.
As Ana Rosa Rama explains, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and surgery show at present "limited" results in advanced stages of cancer. "That is why it is urgent to find new therapies, and gene therapy has emerged as a potentially powerful therapeutic platform." Her work has shown that "it is possible to use gene therapy as an aid to chemotherapy, improving its results when it comes to attacking cancer, thus allowing the dosage of agents to be reduced and contributing to a reduction in side effects for the patient."
In order to understand how the E gene works, the researchers conducted studies using various techniques. The results indicate that the E gene's mechanism of action is to induce apoptosis (cell death), possibly through mitochondrial injury.
Therefore, they stress that "this new E gene appears as an ideal candidate to be transfected into tumour cells in order to induce apoptosis, possibly through mitochondrial activation, and to increase the sensitivity of these cells to the action of the drug developed specifically to act on them."
The results of this research suggest the possibility of reducing the concentration of chemotherapeutic agents in current use with cancer patients. Thus, in lung cancer cell line A-549, scientists from the UGR achieved a 14% inhibition of tumour growth and reduced by 100 times the dose of Paclitaxel agent when it was combined with gene E. In the case of colon cancer, the results were similar. However, the most relevant fact was found in the breast cancer cell line MCF-7, in which the dose of the chemotherapeutic agent, doxorubicin, was reduced by 100 times, reaching up to a 21% greater inhibition of tumour proliferation when combined with gene E. Currently, researchers from the UGR are in the process of obtaining a patent for gene E.
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Gene therapy
Genetic diseases once considered untreatable are now at the center of innovative therapeutic approaches. Research and development of gene therapies in biotech and pharma aim to directly correct or replace defective or missing genes to combat disease at the molecular level. This revolutionary approach promises not only to treat symptoms, but to eliminate the cause of the disease itself.

Topic world Gene therapy
Genetic diseases once considered untreatable are now at the center of innovative therapeutic approaches. Research and development of gene therapies in biotech and pharma aim to directly correct or replace defective or missing genes to combat disease at the molecular level. This revolutionary approach promises not only to treat symptoms, but to eliminate the cause of the disease itself.