Key mucosal immune response mechanism identified
Advertisement
A key mechanism involved in immune surveillance in the intestinal system is described by a team of researchers at RIKEN and Yokohama City University. Their research will appear in Nature and could provide new targets for oral vaccines for infectious diseases and allergies.
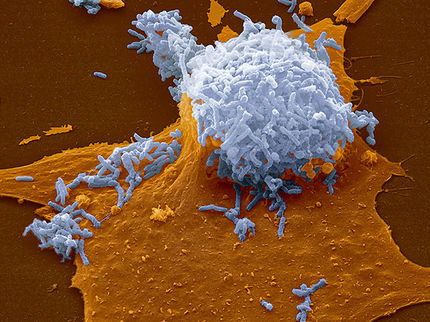
The mucosal immune forms the largest part of the entire immune system and protects the body from pathogens and foreign particles by secreting the antibody Immunoglobin A (IgA). Specialized cells called microfold cells (M cells) capture and deliver foreign particles through the epithelial layer to lymphoid structures deeper in the intestinal tissue. This triggers the secretion of the antibodies.
Although this transport process is crucial researchers have struggled to understand it fully due to the relative sparseness of M cells and a lack of a unique marker to identify them.
The team show that the protein, glycoprotein 2 (GP2), on the outer membrane of M cells, acts as a receptor for certain pathogenic bacteria, rapidly instigating immune responses. Experiments demonstrate that in mice, GP2 specifically binds to bacteria such as E. coli and Salmonella by recognizing a component of hairlike structures on the bacterial cell surface.
This first description of the pathway fills a key gap in the understanding of mucosal immune responses. As a target for the development of new oral vaccines, GP2 also offers the hope of an easy-to-administer, cost-effective solution for infectious diseases and allergies.
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous

Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous