Protein complex key in avoiding DNA repair mistakes, cancer
Lymphoma and other cancers may occur when a delicate gene recombination process in antibody-making cells goes awry
Advertisement
As the body creates antibodies to fight invaders, a three-protein DNA repair complex called MRN is crucial for a normal gene-shuffling process to proceed properly, University of Michigan research shows. The discoveries in mice, published in Nature Structural and molecular biology, advance understanding of the immune system and shed light on how B-cell lymphoma and some other cancers may begin.
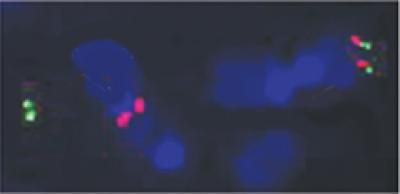
Damaged chromosomes in mouse B cells, left, can be incorrectly repaired and lead to cancer. At right are intact chromosomes.
University of Michigan
U-M scientists found that, when one protein in the MRN complex, Mre11, is absent, mistakes occur in a risky DNA break-and-repair process that routinely occurs in immune system B cells. The process is known as immunoglobulin class switch recombination. Incorrectly repaired DNA can alter the normal action of B lymphocytes and their offspring, whose job is to make antibodies to combat and protect against specific disease-causing microbes and other foreign agents.
"Class switch recombination represents a double-edged sword, being necessary for immune system function, but known to cause cancer when mistakes are made. We now understand that Mre11 and the MRN complex as a whole lie in the middle of this delicate balance," says David O. Ferguson, M.D., Ph.D., the study's senior author and assistant professor of pathology at the U-M Medical School.
The MRN complex consists of three proteins, Mre11, Rad50 and Nbs1. The Ferguson study examined the role of Mre11. The MRN complex is an emerging area of interest in medical science. MRN appears to be a key force in sensing and repairing DNA damage. In the DNA of cells throughout the body, damage known as double strand breaks occurs frequently, especially as people grow older. External causes such as exposure to toxic substances or ionizing radiation, or forces inside the body such as oxidative stress, can cause the breaks. Mistakes in the repair of breaks can lead to cancer.
Original publication: Nature Structural and Molecular Biology 2009
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous

Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous