BMG Labtech
Verifying SPARCL Performance on the CLARIOstar Equipped for Reading at Time of Injection
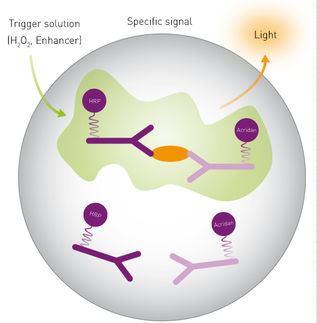
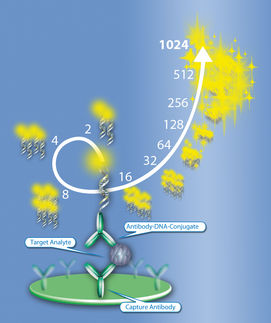
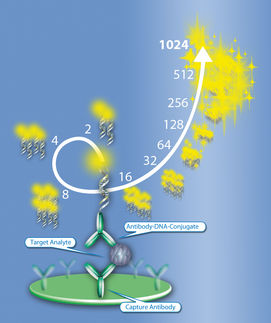
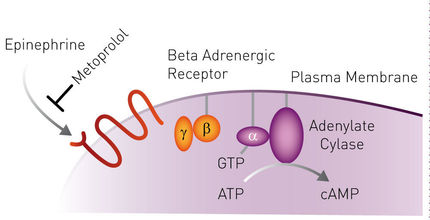
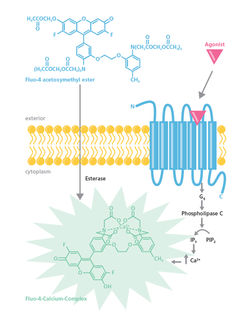
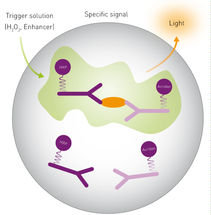
SPARCL refers to an immunoassay that does not require washing steps. An analyte in solution is detected by binding two antibodies: one is coupled to horse radish peroxidase (HRP), the other is coupled to the HRP substrate Acridan.
In presence of the analyte, binding of both antibodies brings enzyme and substrate into proximity. The enzymatic reaction is started by the addition of H2O2, which immediately produces a light proportional to the amount of analyte. Thus, SPARCL assays require to be read at the same time as injection of the trigger solution.
The CLARIOstar® microplate reader equipped with the dedicated H3 injection needle for simultaneous injection and reading fulfils this task. The analyte IgG was detected down to a concentration of 45 ng/ml in 96 wells and down to 15.6 ng/ml in 384 well format. BMG LABTECHs MARS analysis software facilitates subsequent calculation of analyte concentration.
Advertisement
White Paper classification
White papers on related topics
Products on related topics
Manufacturers of similar products
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous

Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous