Nanobret ™ -Based Assay for Internalization of cxcr4
Read how GPCRs are studied at endogenous expression levels by employing CRISPR/Cas9.
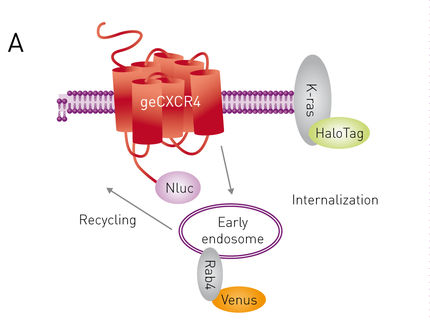
GPCRs are important drug targets requiring receptor-protein interaction and trafficking studies to reveal how they function. Bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) is a versatile tool to study such interactions and trafficking. Hitherto, it is limited by the ectopic expression of labelled interaction partners. CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing overcomes the limitation by enabling endogenous expression of luciferase-labelled proteins. CRISPR/Cas9-edited cells endogenously expressing a CXCR4/NanoLuciferase fusion protein were used in conjunction with β-Arrestin/Venus to monitor receptor activation. Employing two fluorophores fused to a membrane and endosome standing CXCR4-interacting protein, respectively, allowed for monitoring of receptor trafficking. The novel CRISPR/Cas9 technique successfully fused the Nluc BRET donor to endogenously-expressed CXCR4. The resulting protein levels were sufficient to monitor receptor interactions as well as internalization. The internalization assay depends on two acceptor fluorophores whose selective detection was rendered possible by the CLARIOstar’s monochromator.
Download white paper now
Nanobret ™ -Based Assay for Internalization of cxcr4
Read how GPCRs are studied at endogenous expression levels by employing CRISPR/Cas9.

