"Silent" fungus metabolism awakened for new natural products
Fungi wake up to new natural products
US scientists have re-awakened 'silent' metabolic pathways in fungi to reveal a new range of natural products. The research could provide not only a source of new drugs, but a way to "listen to what fungi are saying" to organisms around them.
Fungi produce a wide variety of natural products, including potent toxins - for example, the amanitins, primarily responsible for the toxicity of the death cap fungus - and life-saving drugs such as penicillin. As a result, the genetics of fungi have generated much interest in recent years. Now, Robert Cichewicz and colleagues at the University of Oklahoma, Norman, US, have shown that metabolic pathways that are normally 'silent' can be re-activated to make new compounds, in work published in the Royal Society of Chemistry journal Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry.
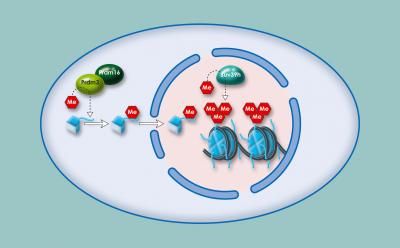
Many fungi have a wealth of genes encoding for far more natural products than they actually produce, says Cichewicz. The explanation is thought to be that when fungi do not need certain compounds, they inhibit the transcription of the DNA that codes for the proteins that make them, preventing their biosynthesis.
Knowing what these mystery compounds are could be very important for the development of new medicines, as well as for helping us to understand the ecological roles that fungi play, claims Cichewicz.
The DNA involved is inhibited by being scrunched up in a globular form called heterochromatin. To activate this DNA and turn on these 'silent' natural product pathways, the team decided to treat fungal cultures with small molecules that interfere with the formation of the heterochromatin - allowing the DNA to be transcripted.
To show their idea in action, the researchers took a culture of Cladosporium cladosporioides, a tidal pool fungus, and treated it separately with 5-azacytidine and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid. Both treatments, says Cichewicz, dramatically changed the natural product output of the fungus, with two completely new natural products being isolated.
The results also have important implications for research into fungi and other microorganisms, explains Cichewicz. Natural products are the means by which fungi 'communicate' with organisms around them, so we are in essence, he says, 'discovering chemical means for listening to what fungi are saying'.
Original publication: Russell Williams et al., Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008.
Most read news
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.