Biogen Idec and Neurimmunie Therapeutics announce alliance to develop treatments for Alzheimer's disease
Advertisement
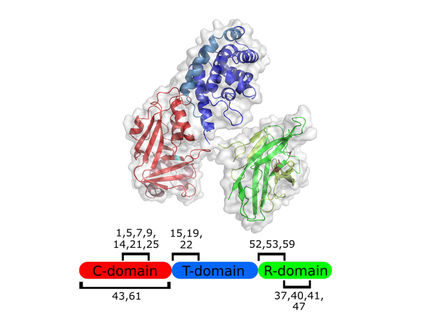
Biogen Idec and Neurimmune Therapeutics AG announced they have entered into an agreement for the worldwide development and commercialization of novel, fully human antibodies for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The alliance will focus on the development of antibodies that bind to amyloid beta (Ab), a pathogenic molecule thought to cause neurodegeneration and loss of cognitive function in AD patients. Currently there are no therapies for AD approved to slow or stop the progression of the disease.
Neurimmune will conduct research to identify potential therapeutic antibodies using the company's Reverse Translational Medicine (RTM) platform. Biogen Idec will be responsible for the development and commercialization of all products. Neurimmune could receive an aggregate of $380M in upfront and success-based milestone payments, as well as a royalty on net sales of any products.
Other news from the department business & finance
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous

Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous