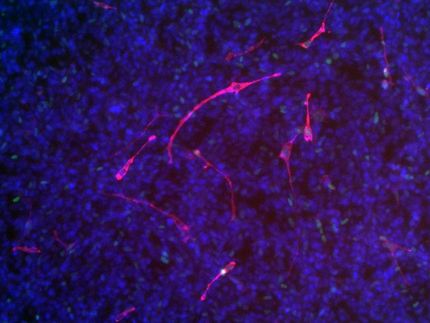
Algeta demonstrates targeted cancer-killing potential of novel alpha particle linked antibodies
Preclinical studies show 227Th-rituximab more effective at killing CD20-positive lymphoma cells than 90Y-tiuxetan-ibritumomab (Zevalin)
Algeta ASA announced that a research paper showing the potential of its TH-1 technology for targeted cancer therapy has been published by "Blood", the official journal of the American Society of hematology (ASH).
Algeta's TH-1 technology links Thorium-227, which emits alpha particles, to cancer-targeting molecules such as antibodies. Alpha-emitting radionuclides are of considerable interest in the treatment of cancer as they are highly destructive to tumour cells but have very short range. Linking this radionuclide to tumour-seeking molecules creates a conjugate with the potential to specifically seek and destroy cancers while leaving surrounding healthy tissues undamaged.
The Blood paper describes how researchers from the Norwegian Radium Hospital (Oslo) in collaboration with Professor Oliver Press at the Fred Hutchison Cancer Research Center (Seattle, USA) and Algeta have linked Thorium-227 to the monoclonal antibody rituximab to create 227Th-rituximab and demonstrated its potent anti-tumour effects.
Rituximab binds to a specific molecule on the cancer cell surface called CD20 and is marketed in USA as Rituxan® by Genentech and Biogen-Idec for the treatment of certain types of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) and rheumatoid arthritis, and as MabThera® by Roche for the treatment of certain types of NHL. Rituximab-based therapies generated global sales of nearly $6 billion in 2006.
In in vitro studies 227Th-rituximab killed CD20-positive lymphoma cells at low doses (Bq/ml) while in preclinical models, a single injection of 227Th-rituximab induced complete tumor regression in up to 60% of tumours without apparent toxicity.
According to the company, therapy with 227Th-rituximab was significantly more effective than the control radioimmunoconjugate 227Th-trastuzumab, which does not bind CD20, and the standard beta particle emitting radioimmunoconjugate for CD20-positive lymphoma, Zevalin® (90Y-tiuxetan-ibritumomab), which is marketed by Biogen-Idec.
Original publication: Dahle, J. et al.; "Targeted cancer therapy with a novel low dose rate alpha-emitting radioimmunoconjugate"; Blood 2007.
Most read news
Other news from the department research and development

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Combating cancer's double whammy - New research to fight life-threatening blood clots in cancer patients

What determines whether breast cancer cells can form metastases? - Reprogrammed clones metastasize less
Livatag follow up demonstrates significant survival increase in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients

Giant snails as pets can be dangerous - They are both scary and fascinating at the same time. Giant snails are becoming increasingly popular as pets. Now researchers are warning
I was here first! This is how hepatitis C inhibits hepatitis E - A single protein from one virus can prevent infection with another virus in cell culture
ORYX Presents Positive Phase I/IIa Data with Therapeutic Vaccine MicOryx
A new path through the looking-glass - Innovative experimental scheme can create mirror molecules
MIT biologists find that restoring the gene for cancer protein p53 slows spread of advanced tumors
Domainex to Invest in its Drug Discovery Services and Internal Oncology Pipeline in 2011
For a Better Contrast - Rare earth orthoferrite LnFeO3 nanoparticles for bioimaging

A novel textile material that keeps itself germ-free