First DNA sequence from a single mitochondria
DNA sequences between mitochondria within a single cell are vastly different, found researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. This knowledge will help to better illuminate the underlying mechanisms of many disorders that start with accumulated mutations in individual mitochondria and provide clues about how patients might respond to specific therapies.
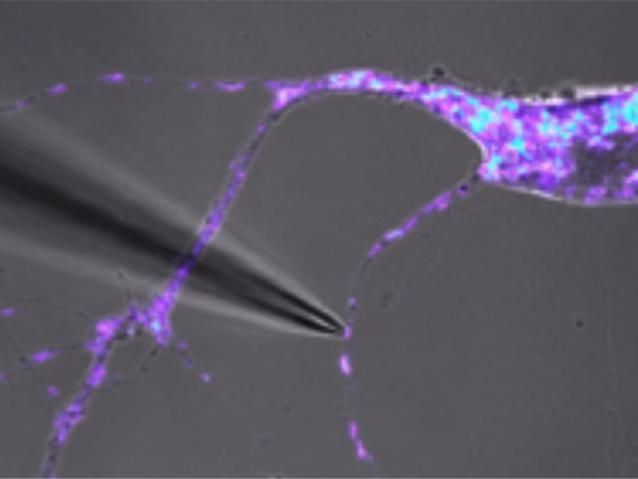
Manual isolation of a single live mitochondria. The mitochondria can be seen under a microscope where a thin glass tube can be used to isolate the mitochondria from the dendrite region of the mouse neuron.
Jacqueline Morris and Jaehee Lee, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania
Mitochondria, a component of cells that have their own DNA (mtDNA), produce energy for the body, among other functions. One mitochondrion can contain 10 or more different genomes with hundreds to thousands of individual mitochondria residing in each cell. A number of mitochondrial diseases arise from mutations accumulating in mtDNA. For example, these mutations have been found in colorectal, ovarian, breast, bladder, kidney, lung, and pancreatic tumors.
Using methods developed in the lab of senior author James Eberwine, PhD, a professor of Systems Pharmacology and Translational Therapeutics, the investigators extracted single mitochondrion and then extracted its mtDNA. They compared mutations present in single mitochondrion in individual mouse and human neurons and found that mouse cells had more accumulated mutations compared to human cells. Because of this finding that mutations accumulate at a different rate in mice versus humans, Eberwine notes that one important take away from the study is to ensure that mitochondrial diseases or potential therapeutics in cells are examined in models where the mutations parallel those that occur in humans.
The process of mtDNA mutations accruing over a lifetime most likely happens somewhat differently in each person. The study addressed similarities and differences in discrete mtDNA in the same cell and also between cell types such as neurons and astrocytes in the brain. "By being able to look at a single mitochondrion and compare mutational dynamics between mitochondria, we will be able to gauge the risk for reaching a threshold for diseases associated with increasing numbers of mitochondrial mutations." For instance, these data may improve diagnosis for neurological diseases, potentially allowing physicians to detect cells that could become diseased or pinpointing patients who may develop certain conditions. This is particularly likely for conditions that more commonly strike the elderly in which mtDNA mutations have been found to accumulate with age.
In the future, the researchers plan to use this knowledge to find ways to slow the rate of mtDNA mutation accumulation in hopes of halting disease progression. "This roadmap of the location and number of mutations within the DNA of a mitochondrion and across all of a cell's mitochondria is where we need to start," Eberwine said.
Original publication
Jacqueline Morris, Young-Ji Na, Hua Zhu, Jae-Hee Lee, Hoa Giang, Alexandra V. Ulyanova, Gordon H. Baltuch, Steven Brem, H. Isaac Chen, David K. Kung, Timothy H. Lucas, Donald M. O’Rourke, John A. Wolf, M. Sean Grady, Jai-Yoon Sul, Junhyong Kim, James Eberwine; "Pervasive within-Mitochondrion Single-Nucleotide Variant Heteroplasmy as Revealed by Single-Mitochondrion Sequencing"; Cell Reports; 2017
Most read news
Original publication
Jacqueline Morris, Young-Ji Na, Hua Zhu, Jae-Hee Lee, Hoa Giang, Alexandra V. Ulyanova, Gordon H. Baltuch, Steven Brem, H. Isaac Chen, David K. Kung, Timothy H. Lucas, Donald M. O’Rourke, John A. Wolf, M. Sean Grady, Jai-Yoon Sul, Junhyong Kim, James Eberwine; "Pervasive within-Mitochondrion Single-Nucleotide Variant Heteroplasmy as Revealed by Single-Mitochondrion Sequencing"; Cell Reports; 2017
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.