3-D axon assemblies pave the way for drug discovery
Advertisement
axons are the structures through which neurons transmit information to other cells. In the body, they aggregate to form fascicles. Several technologies allow scientists to generate and study single axons in the lab, but none are effective at creating nerve fascicles. A collaboration between researchers in Japan and the United States has led to a new microdevice that successfully forms fascicles in the lab. The report is expected to provide important insights on brain development and disease.
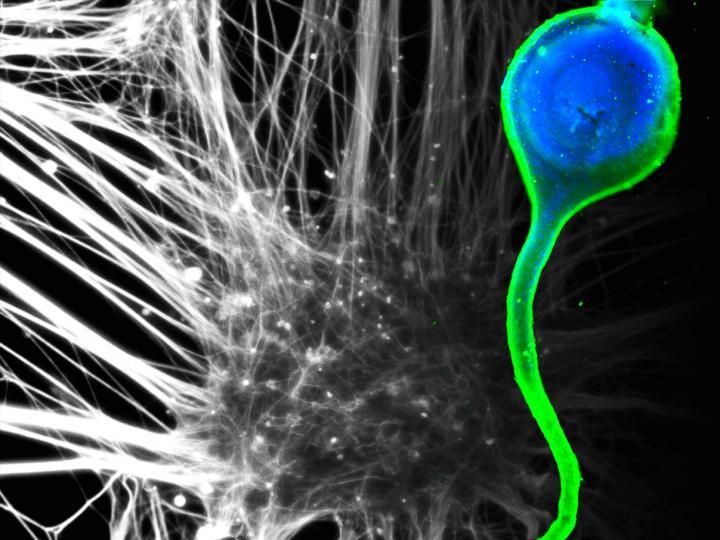
Motor nerve-like tissue (right) was generated using human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived motor neurons (left).
2017 Jun Kamei and Yoshiho Ikeuchi, Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo
"We know that growing axons form fascicles, but we do not know how fascicles form," says Yoshiho Ikeuchi, a lecturer at the Institute of Industrial Science at the University of Tokyo and senior author of the study.
Many scientists have examined axon development and degeneration in two-dimensional (2D) systems. However, it is becoming increasingly apparent that the fascicle's 3D structure has an essential role in axon function. Because fascicles are disrupted in many neurodegenerative diseases such as ALS, the research group theorized that understanding their formation could give clues on the prevention of a number of diseases.
To form axon fascicles, the research teams manufactured a microdevice in which human neurons derived from induced pluripotent stem cells were injected. What allowed for the formation of the fascicles was the preparation of neural spheroids and a channel narrow enough to align axons, which let them bind to each other.
Spheroids were placed inside the chamber of the device. Axons grew from these spheroids, with some entering the microchannel. Upon this entry, other axons would spontaneously follow, leading to the formation of fascicles that showed properties consistent with those seen in brains. What molecular signaling caused the spontaneous entry remains unexplained, but fascicles were detected in more than 90% of experiments, convincing the researchers the value of the microdevice design.
"The device gives us a means to investigate which factors are responsible for the fascicle assembly," says Ikeuchi.
Accordingly, they simulated neurodegenerative conditions by introducing into the channels peroxide, and the fascicles responded with morphological changes.
These findings and the relative ease of the experiments suggest the microdevice will be applicable to testing experimental drug compounds that prevent fascicle degeneration caused by disease.