Pioneering discovery of an odor-detecting receptor enhancer
Advertisement
Each odor-detecting neuron (referred to as olfactory sensory neuron from here on), chooses a single odorant receptor gene from a fairly large number of options that are split into class I (fish-like) and class II (terrestrial-specific) odorant receptors. This strict selectiveness of sensory neurons is in part due to enhancers (DNA sequences that enhance transcription of a gene when bound by specific protein), which remain poorly understood. Understanding enhancer functions is of great interest due to their importance in gene expression as well as evolution and disease. However, they have not been sufficiently studied because they cannot be easily predicted from DNA sequences or chromosome modifications nor can they be easily identified.
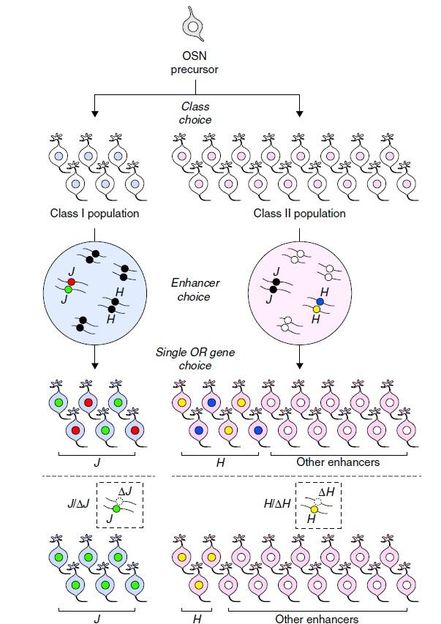
Olfactory sensory neurons express either a class I or class II olfactory receptor gene in order to express either class I (blue) or class II (pink) olfactory sensory neurons. The enhancer is chosen based on the category, and class I sensory neurons activate one enhancer allele of the J element (green or red circle). On the other hand, class II sensory neurons activate other class II enhancers (white circle, H element is yellow or blue).
Junji Hirota
The findings are especially important as they highlight the discovery of a regulatory sequence, termed the J element, that controls class I gene expression of many more genes than the counterparts that regulate class II gene expression. This extraordinary long-range regulation has never been seen before. The researchers also report that it is evolutionarily conserved across mammalian species, ranging from the most primitive mammal, the platypus, to humans. This may be especially useful as it sheds light onto why class I genes remain on a single region on one chromosome during mammalian evolution, while class II genes do not.
Based on genetic evidence, the findings also highlight the concept of allelic exclusion, or the expression of just one copy of a gene and not the other. This is especially important for the J element, as it shows that its activity determines which copy of a gene is expressed. This is a novel mechanism of expression of these receptor genes that is based on the gene regulatory region that determines if genes will be turned on or off.
The study was a collaborative effort between Tokyo Tech, the University of Tokyo, Nihon BioData Corporation and RIKEN Brain Science Institute. Junji Hirota at Tokyo Tech and team focused on discovering a long-range enhancer for a large gene cluster, finding an evolutionary conserved sequence motif in mammalian evolution, and elucidating enhancer-dependent allelic preference or exclusion mechanism for odor-detecting receptor genes. Their findings point to a conserved sequence among mammalian genomes that was only present in the J element and not in any other class II elements. They speculate that the investigation of factors that bind this specific element could help in elucidating molecular mechanisms that drive the selective J-element dependent gene expression.