Sticking instead of stitching
Nanoparticles that stick wounds together
Advertisement
In spite of medical advances, wound-related complications arising after operations can still be life-threatening. In order to avoid these complications in the future, a new nanoparticle-based tissue glue has been developed by researchers at Empa.
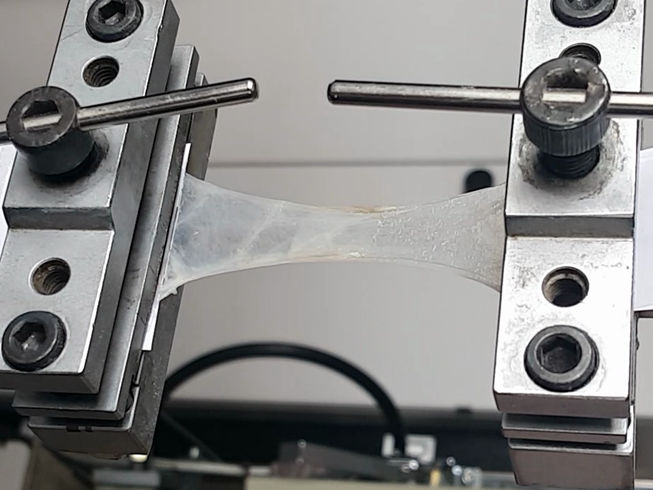

Pig intestines were used for testing the new nanoparticle-based tissue glue
Empa
There are internal and external areas of the body where it is difficult to apply stitches. Although medical science has made considerable progress in recent decades, complications still arise, especially after operations. In some cases, these are fatal. Particularly with internal wounds, there is a risk of haemorrhage, which is difficult to treat because it is not easy to stitch or apply a plaster to internal wounds.
Now there is an innovative tissue glue, the purpose of which is to help to close wounds optimally in areas where they are difficult to locate or access, and to avoid diffuse and often life-threatening haemorrhages. The idea of a tissue glue is not new: conventional glues consist primarily of fibrin, a protein produced by the body which plays a key role in clotting the blood. Fibrin is not only very expensive, but can also trigger immune responses, which frequently result in serious complications.
An adhesive that also heals
As described recently in the specialist literature, it has now been discovered that nanoparticles have an adhesive property, known as "nano-bridging". In the study in question, researchers used silica (silicon dioxide) and iron oxide nanoparticles to stick pieces of tissue together. Under Inge Herrmann's leadership, researchers at Empa used this innovative principle to develop a tissue glue to be used in the future for various operations and complaints. They created nanoparticles from various material combinations, with a view to making the glue bioactive.
And they succeeded. A combination of glue and bioglass makes the blood clot more quickly at the location of the wound. Depending on the combination of the elements silicon, calcium, sodium and phosphorus, bioglass has various different properties. If the ideal combination is achieved, this will open up completely new treatment possibilities. Depending on the formula, for example, bioglass may form effective bonds with bones or soft tissue. The researchers also ensured that none of the materials used is harmful to health.
First study of potential surgical use is published
Doctors helped the Empa research team to develop the tissue glue. For example, they expressed their wish to use the glue for intestinal tears. If the intestinal wall is damaged, tissue-damaging substances may leak out – so a glue of this kind would be ideal. In their study, the Empa researchers aimed to fulfil the doctors' wish. Martin Matter, a doctoral candidate in Herrmann's team and lead author of the study, used pig intestines to test the new glue. He investigated its capacity to glue the intestines together in the Empa textile laboratory in St. Gallen, by using a machine that usually tests the tear strength of materials. The first findings were extremely promising. So promising, in fact, that this line of research is still being pursued. Herrmann is convinced that there are further exciting possibilities for the glue if it is given additional properties.