Molecular Force Sensors
proteins are often considered as molecular machines. To understand how they work, it is not enough to visualize the involved proteins under the microscope. Wherever machines are at work mechanical forces occur, which in turn influence biological processes. These extremely small intracellular forces can be measured with the help of molecular force sensors. Now researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry in Martinsried have developed molecular probes that can measure forces across multiple proteins with high resolution in cells.
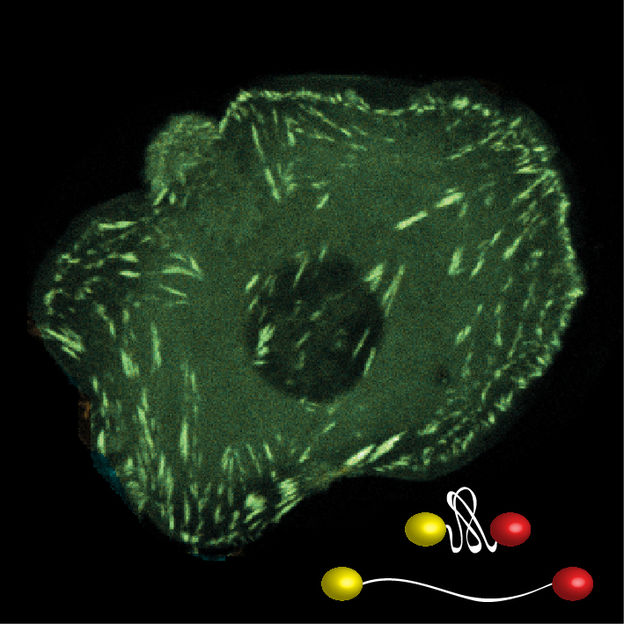
The development of novel, fluorescence-based biosensors, which unfold in response to mechanical loads, allows the evaluation of molecular forces across specific structures within living cells.
© MPI für Biochemie
When proteins pull on each other, forces in the piconewton range are generated. Cells can detect such mechanical information and modulate their response depending on the nature of the signal. Adhesion proteins on the surface of cells, for instance, recognize how rigid their environment is to adjust the protein composition of the cell accordingly. To measure such tiny forces, the group of Molecular Mechanotransduction at the Max Planck Institute is developing molecular force sensors. “These small measuring instruments work along the lines of a spring scale,” says Carsten Grashoff, head of the research group.
The innovative probes consist of two fluorescent molecules that are connected by a sort of molecular spring. When a force of just a few piconewton acts on the molecule, the spring stretches, and this change can be detected using a special microscopic method. “We’re now able to measure the mechanics of several molecules simultaneously,” Carsten Grashoff explains. In contrast to previous experiments, the scientists are not only able to determine which proteins, but also how many of them are under force at any given moment.
“In a tug-of-war, many people pull on a rope with different strengths. Some may take it easy and let the person in front do the work. Proteins work in a very similar manner. We can now determine which proteins contribute to cellular force development and what percentage of those molecules are actually involved,” Grashoff explains. Moreover, the force sensitivity has been improved, with the method allowing precise measurements in the range of three to five piconewton. “As with the development of new microscopes, we are striving to attain ever better resolutions, and that is what we have achieved here,” Grashoff continues.
Thanks to the universal nature of cellular mechanics, the new sensors should be valuable to address a whole range of biological research questions. “Cancer research is an obvious field of application, since it has long been known that tumour cells have advantages in rigid tissues. The sensors could also give new insights into the mechanisms underlying muscle and skin diseases,” Grashoff predicts.
Original publication
P. Ringer, A. Weiβl, A.-L. Cost, A. Freikamp, B. Sabass, A. Mehlich, M. Tramier, M. Rief and C. Grashoff; “Multiplexing molecular tension sensors reveals piconewton force gradient across talin-1”; Nature Methods; September 2017