The carotenoid transfer between 2 proteins
Specialists from the biological faculty of Moscow State University have studied the way the photoactive orange carotenoid protein (OCP) exchanges carotenoid with proteins of similar structure. The discovery will boost the development of OCP-based antioxidant drugs aimed at protecting healthy cells during cancer treatment.
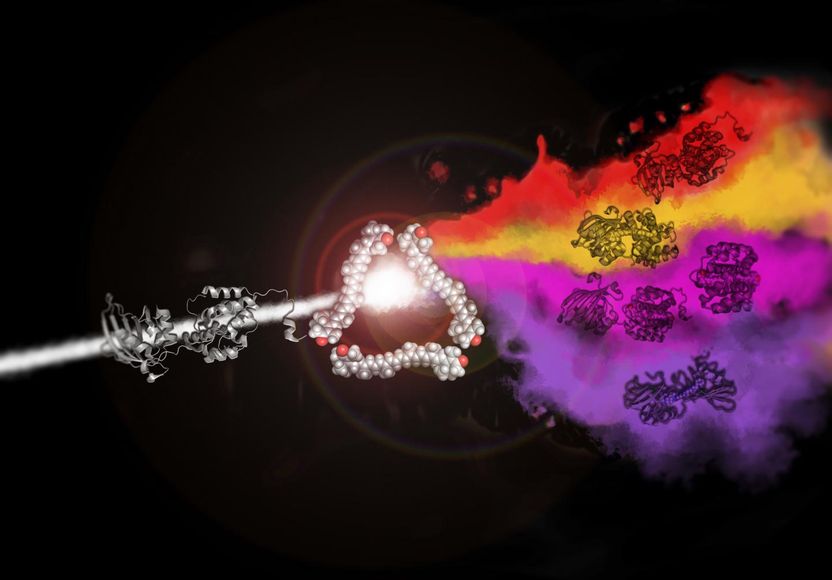
"Cover art" for this article reminds of the cover of the album "The Dark Side of the Moon" by Pink Floyd. It shows how red, purple, orange and violet proteins can be obtained from a colorless protein and one type of a carotenoid.
Eugene Maksimov
The orange carotenoid protein (OCP) is a small water-soluble protein that serves as an excitation energy quencher in cyanobacteria: it reduces energy transfer in the photosynthetic apparatus under high light conditions. Cyanobacteria are one of the earliest organisms on the Earth capable of photosynthesis. Our planet owes them high concentration of oxygen in the atmosphere.
Under strong light orange carotenoid protein changes its structure and interacts with antennas to prevent formation of reactive oxygen species. Carotenoids are long hydrocarbon molecules with a large number of double bonds, which serve as photosensitive chromophores. The color of carotenoid depends on the protein state.
Previously, the biologists from the Moscow State University have described the structure and properties of the OCP domains which appeared to be capable of binding the carotenoid into a complex of bright violet color. One of the interesting and previously unknown properties of the orange carotenoid protein is the ability to transmit the carotenoid to other proteins with a similar structure.
"We studied the interaction of carotenoid-containing violet C-domains of the OCP with a colorless apo form of the OCP. As a result of the interaction, the colorless apo form of the OCP became orange and photoactive (capable of changing its structure and color). The carotenoid transfer process simulates the process of assembling a photoactive protein from a protein matrix and a chromophore (carotenoid)," said Dr. Eugene Maksimov, senior researcher at the Laboratory of Biophotonics.
The discovered transfer reaction of a hydrophobic carotenoid molecule between two water-soluble proteins gives us several interesting opportunities. This mechanism will allow us create water-soluble protein complexes to deliver antioxidant carotenoid to cells that need protection from the reactive oxygen species: for example, to the healthy tissue during photodynamic cancer therapy. The photoactive properties of the complex will be useful in molecular thermometers: their color will show the difference in temperature between the parts of the cell.
Original publication
Original publication
Eugene G. Maksimov, Nikolai N. Sluchanko, Yury B. Slonimskiy, Kirill S. Mironov, Konstantin E. Klementiev, Marcus Moldenhauer, Thomas Friedrich, Dmitry A. Los, Vladimir Z. Paschenko, Andrew B. Rubin; "The Unique Protein-to-Protein Carotenoid Transfer Mechanism"; Biophysical Journal; 2017
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents

Wacker Biotech B.V. - Amsterdam, Netherlands

Spices and herbs: Ingredients which may pose a health risk
A peptide against cannibalism - A small molecule safeguards roundworm larvae against parental attacks
The_Fertility_Society_of_Australia
Cells that sense light without seeing
Discovery opens door to therapeutic development for FSH muscular dystrophy
ThromboGenics Announces that Microplasmin Meets Primary Endpoint in Phase III Trial for Vitreomacular Adhesion - Highly significant trial result (p=0.003) demonstrates the potential of microplasmin in the treatment of retinal disease
Combination Pack Battles Cancer - Nanoparticles with multifunctional drug precursor for synergistic tumor therapy
Immune response to Sars-Cov-2 following organ transplantation - Even patients with suppressed immune systems can achieve a strong immune response to Sars-Cov-2: A test helps to adapt therapy following an infection
Picturing pain could help unlock its mysteries and lead to better treatments





















































