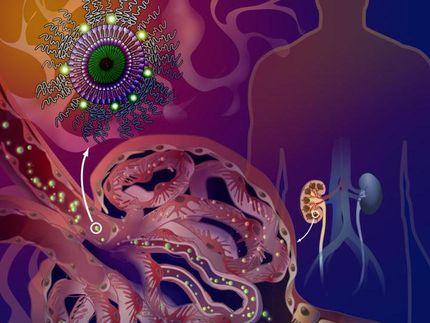
New triggerable, tough hydrogels could make drug-releasing systems safer
Drug-releasing devices that reside in the stomach for extended periods of time make it easier for patients to receive their full course of treatment. Instead of having to take a pill every day for a long period of time, a drug-delivery vehicle that slowly releases individual doses of medication could be administered once but provide medication for weeks or months.
Swallowable drug delivery systems are typically made of tough plastics such as thermoplastics or thermosets, but these materials present safety concerns in that they can cause physical obstructions in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and are difficult to remove in the case of an allergic reaction. Instead, hydrogels, which are softer and potentially more biocompatible, are an appealing alternative for gastric resident systems. In a new study researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital, Massachusetts Institute of Technology and the Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research created a novel hydrogel material. The hydrogel is tough and triggerable, meaning it can withstand the forces of the GI environment and can be triggered to dissolve using an external stimulus.
"A lot of our work is centered on the concept of making it easier for patients to take their medications. A triggerable, tough hydrogel allows us to create systems that can easily deliver drugs over long periods of time while simultaneously addressing several of the chief safety concerns of these types of devices," said corresponding author Carlo "Gio" Traverso, MB, PhD, of the Division of Gastroenterology at BWH.
Hydrogels are appealing for a number of reasons. They are mainly composed of water so they can shrink in their dry state to become small enough to swallow, and then can expand and swell in the stomach to avoid passing into the small intestine. They can also be loaded with medicine and release it in a controlled manner.
However, the challenge with classic hydrogels is that they are relatively weak. The gastric cavity experiences significant forces associated with contractions of the stomach, so the new hydrogels need to be tough enough to withstand the strain.
Hydrogels are composed of a "net" of polymer chains. To toughen them up, the researchers created a double network hydrogel composed of two interwoven polymer nets. The next step was to make these hydrogels dissolvable in case the drug-delivery system needed to be removed quickly. They designed the hydrogel to be triggered to dissolve if the biocompatible agents EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) and GSH (glutathione) are consumed. The combination of EDTA and GSH can quickly break down the cross-links holding the two polymer nets together.
The researchers tested the tough, triggerable hydrogels in a large animal model which demonstrated the potential of this material.
"This material represents one of the first examples of a triggerable, tough hydrogel and could thus be used in many different applications such as supporting stem cell growth in the lab or in bariatric medicine," said Traverso. The next step in their research will be additional pre-clinical studies to further test the safety and stress resistance of the hydrogels before they can be used in people.
"We are really excited about the development of this new family of hydrogels and their potential to permit numerous new medical applications," says Robert Langer, Professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Original publication
Jinyao Liu, Yan Pang, Shiyi Zhang, Cody Cleveland, Xiaolei Yin, Lucas Booth, Jiaqi Lin, Young-Ah Lucy Lee, Hormoz Mazdiyasni, Sarah Saxton, Ameya R. Kirtane, Thomas von Erlach, Jaimie Rogner, Robert Langer & Giovanni Traverso; "Triggerable tough hydrogels for gastric resident dosage forms"; Nature Comm.; 2017
Most read news
Original publication
Jinyao Liu, Yan Pang, Shiyi Zhang, Cody Cleveland, Xiaolei Yin, Lucas Booth, Jiaqi Lin, Young-Ah Lucy Lee, Hormoz Mazdiyasni, Sarah Saxton, Ameya R. Kirtane, Thomas von Erlach, Jaimie Rogner, Robert Langer & Giovanni Traverso; "Triggerable tough hydrogels for gastric resident dosage forms"; Nature Comm.; 2017
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
List_of_subjects_in_Gray's_Anatomy:_XI._Splanchnology
Self-surgery
Genetic Technologies grants third license to Monsanto
Kyasanur_forest_disease

New technology offers fast peptide synthesis
Chemotherapy timing is key to success - Nanoparticles that stagger delivery of 2 drugs knock out aggressive tumors in mice

New financing round at oncgnostics GmbH close
Night_owl_(person)
Enigmatic gene critical for a healthy brain