Mycobacteria use protein to create diverse populations, avoid drugs
Advertisement
Subgroups of tuberculosis (TB)-causing bacteria can persist even when antibiotics wipe out most of the overall population. The need to eliminate these persistent subpopulations is one reason why TB treatment regimens are so lengthy. Now, researchers have shown that a single protein allows mycobacteria to generate diverse populations that can avoid TB drugs. The protein may be a target for intervention; blocking it might result in less mycobacterial diversity and shorten TB treatment courses. The research was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and infectious diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health.
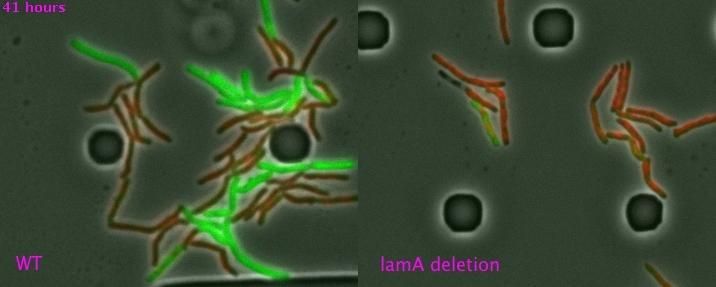
Mycobacteria in left panel have lamA gene. When exposed to an antibiotic, some (red) are killed, while others (green) continue to grow and divide. Cells on the right are missing lamA and are killed faster and more uniformly by the antibiotic.
Eric J. Rubin and E. Hesper Rego
Eric J. Rubin, M.D., Ph.D., of Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, and E. Hesper Rego, Ph.D., of Yale University School of Medicine, and their coworkers first studied Mycobacterium smegmatis, a close relative of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), the microbe that causes TB. Using fluorescent reporter molecules and time-lapse microscopy, they examined individual cells as they grew and divided. Mycobacteria can generate daughter cells through asymmetric growth, resulting in genetically identical, but physiologically diverse, populations. The mechanisms underlying this ability and the extent to which the cells' size, growth rate and other physiological properties relate to survival in mycobacterial populations were not well understood.
Dr. Rubin and colleagues determined that the protein product of a single gene, lamA, is a member of the protein machinery that is active when mycobacteria divide. The protein--which is not known to exist in other rod-shaped bacteria or other organisms--seems to allow for asymmetrical growth in new mycobacterial cells made during cell division. The asymmetrical growth leads to bacteria with wide variations in physiological properties and susceptibility to antibiotics.
In experiments using Mtb, the scientists found that mycobacteria without lamA formed far less diverse bacteria with more uniform susceptibility to antibiotics. When exposed to the front-line TB drug rifampicin, for example, Mtb cells lacking lamA were less able to survive than wildtype bacteria. In the future, it may be possible to devise ways to inhibit lamA or its protein. This could lead to reduced variation in Mtb populations and, potentially, to more uniform vulnerability to drugs, according to the scientists.