Not such a 'simple' sugar
Glucose may help fight cancer and inflammatory disease
Advertisement
glucose - commonly referred to as a 'simple' sugar - may actually be crucial in the fight against cancer and inflammatory disease as scientists have just discovered a new role in which it stimulates cells that work on the front line in the fight against tumours and infection.
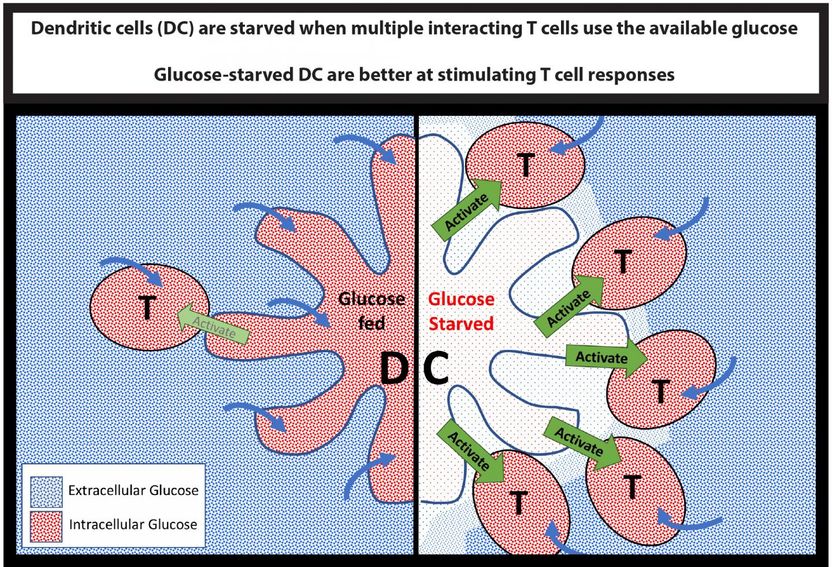
Cartoon diagram indicating the glucose signaling pathway.
Professor David Finlay, Trinity College Dublin
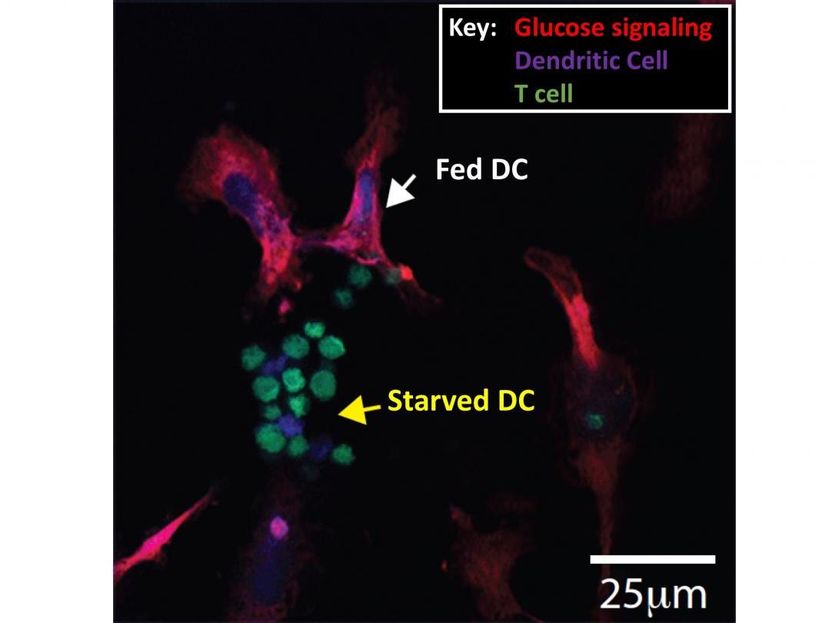
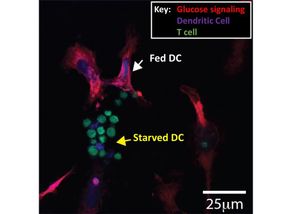
Confocal image showing glucose signaling pathway.
Professor David Finlay, Trinity College Dublin
Glucose, which is generated from the food that we eat, is the most important fuel used in our bodies as our cells use it to generate energy and for growth and division. The cells of our immune system become very active during an immune response, such as when responding to infection, and as a result they tend to have high demands for glucose. Unsurprisingly, when immune cells are starved of glucose, as might occur within tumours for instance, they become dysfunctional.
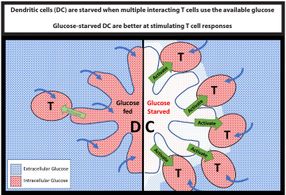
However, new research led by scientists at Trinity College Dublin shows that the immune cells that monitor our bodies for signs of danger (dendritic cells) are different -- when they are starved of glucose they actually become better at stimulating the vital players in the immune response (T lymphocytes).
The scientists believe this opens the door to new therapeutic possibilities to regulate immune responses to cancers and other immune-related diseases.
Ussher Assistant Professor in Cancer Biology, David Finlay, led the team whose work has just been published.
Dr Finlay said: "It is becoming clear that glucose is an important signaller in our immune system, in that cells that have access to glucose behave very differently to those that do not. We have discovered that dendritic cells are actually better at stimulating immune responses when starved of glucose, which is not the case for any of the other immune cells that have been analysed."
"The discovery that T cells and dendritic cells compete with each other for glucose offers a new and exciting insight into how glucose can regulate dendritic cell function. We hope that by better understanding how nutrients such as glucose control the immune response, we can go on to develop new therapies to tackle a host of debilitating immune-related diseases."