Bacteria with Midas touch for efficient gold processing
Special 'nugget-producing' bacteria may hold the key to more efficient processing of gold ore, mine tailings and recycled electronics, as well as aid in exploration for new deposits, University of Adelaide research has shown.
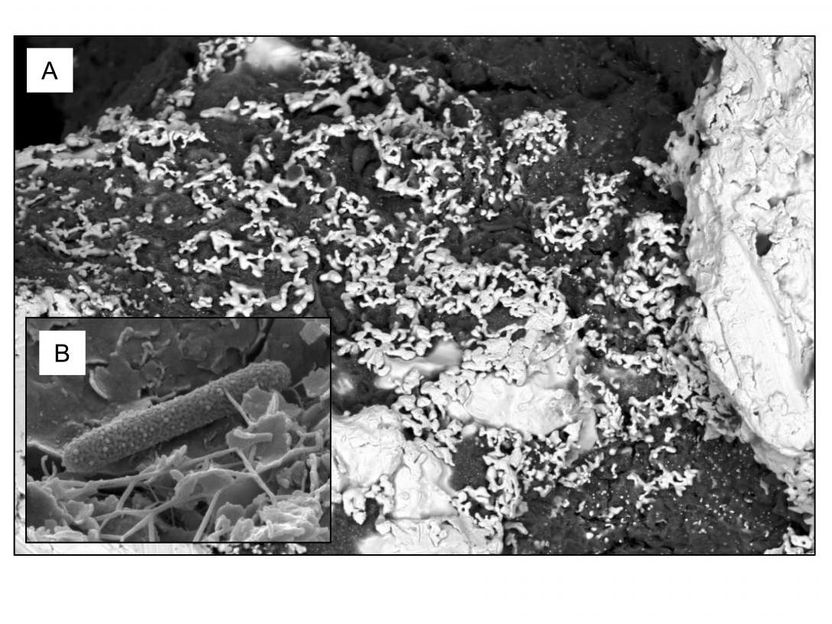

This is an electron microscope images of a gold grain surface (A) and a bacterial cell on the surface of the gold (B).
Adelaide Microscopy
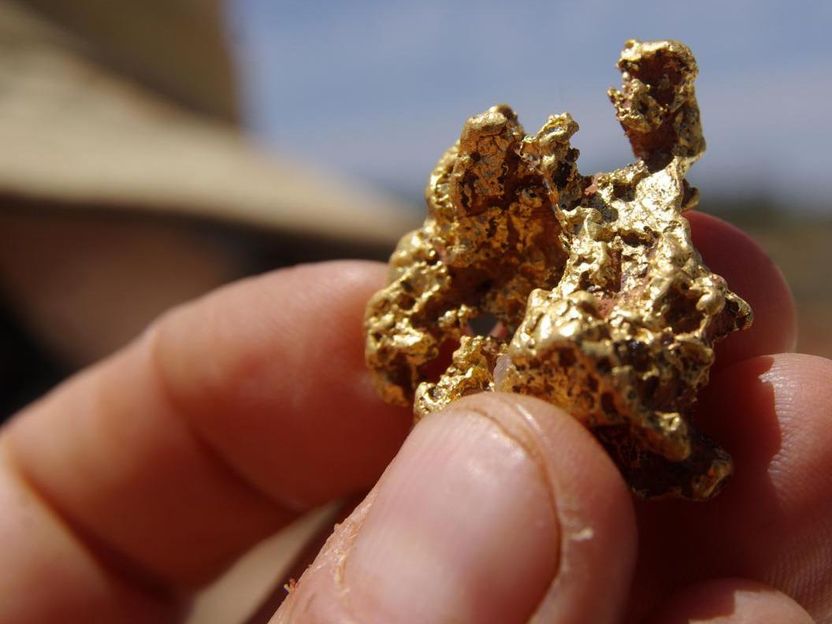

This is a gold nugget from the field.
Joel Brugger


For more than 10 years, University of Adelaide researchers have been investigating the role of microorganisms in gold transformation. In the Earth's surface, gold can be dissolved, dispersed and reconcentrated into nuggets. This epic 'journey' is called the biogeochemical cycle of gold.
Now they have shown for the first time, just how long this biogeochemical cycle takes and they hope to make to it even faster in the future.
"Primary gold is produced under high pressures and temperatures deep below the Earth's surface and is mined, nowadays, from very large primary deposits, such as at the Superpit in Kalgoorlie," says Dr Frank Reith, Australian Research Council Future Fellow in the University of Adelaide's School of Biological Sciences, and Visiting Fellow at CSIRO Land and Water at Waite.
"In the natural environment, primary gold makes its way into soils, sediments and waterways through biogeochemical weathering and eventually ends up in the ocean. On the way bacteria can dissolve and re-concentrate gold - this process removes most of the silver and forms gold nuggets.
"We've known that this process takes place, but for the first time we've been able to show that this transformation takes place in just years to decades -- that's a blink of an eye in terms of geological time.
"These results have surprised us, and lead the way for many interesting applications such as optimising the processes for gold extraction from ore and re-processing old tailings or recycled electronics, which isn't currently economically viable."
Working with John and Johno Parsons (Prophet Gold Mine, Queensland), Professor Gordon Southam (University of Queensland) and Dr Geert Cornelis (formerly of the CSIRO), Dr Reith and postdoctoral researcher Dr Jeremiah Shuster analysed numerous gold grains collected from West Coast Creek using high-resolution electron-microscopy.
Published in the journal Chemical Geology , they showed that five 'episodes' of gold biogeochemical cycling had occurred on each gold grain. Each episode was estimated to take between 3.5 and 11.7 years -- a total of under 18 to almost 60 years to form the secondary gold.
"Understanding this gold biogeochemical cycle could help mineral exploration by finding undiscovered gold deposits or developing innovative processing techniques," says Dr Shuster, University of Adelaide. "If we can make this process faster, then the potential for re-processing tailings and improving ore-processing would be game-changing. Initial attempts to speed up these reactions are looking promising."
The researchers say that this new understanding of the gold biogeochemical process and transformation may also help verify the authenticity of archaeological gold artefacts and distinguish them from fraudulent copies.