Images of pathogens’ tiny ‘syringes’ captured
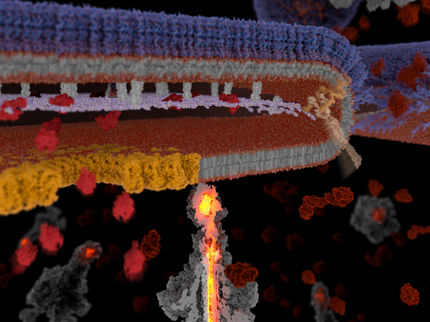
Salmonella and many other bacterial pathogens use a nano syringe-like device to deliver toxic proteins into target human cells. Now scientists at Yale and University of Texas Medical School-Houston have used cryo-electron tomography to reveal the molecular structure of this device, which is about 1/1000th the width of a human hair.
The nano-syringe, called Type III protein secretion machine, features an injection point at one end and a sort of staging area at the bottom, where proteins are selected and sorted for delivery into target cells.
“The device is like a stinger and injects ready-made bacterial proteins into mammalian cells to commandeer them for the benefit of the pathogen,” said Jorge Galan , the Lucille P. Markey Professor of Microbial Pathogenesis and co-senior author of the paper.
Knowledge of the structure could help researchers devise new anti-infective strategies against a variety of bacterial pathogens such as Salmonella, Pseudomonas, Escherichia coli, Yersinia pestis, and Chlamydia.
Original publication
Bo Hu, Maria Lara-Tejero, Qingke Kong, Jorge E. Galán, Jun Liu; "In Situ Molecular Architecture of the Salmonella Type III Secretion Machine"; Cell; 2017
Most read news
Original publication
Bo Hu, Maria Lara-Tejero, Qingke Kong, Jorge E. Galán, Jun Liu; "In Situ Molecular Architecture of the Salmonella Type III Secretion Machine"; Cell; 2017
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents