Machine-learning driven findings uncover new cellular players in tumor microenvironment
Involvement of adipocytes in nivolumab response in ipilimumab resistant melanoma patients
Advertisement
New findings presented by CytoReason reveals possible new cellular players in the tumor microenvironment that could impact the treatment process for the most in-need patients - those who have already failed to respond to ipilimumab (anti-CTLA4) immunotherapy. Once validated, the findings could point the way to improved strategies for the staging and ordering of key immunotherapies in refractory melanoma. The data, being presented at the 30th Anniversary American Association for Cancer Research Special AI Conference, also reveals previously unidentified potential targets for future new therapies.
Machine Learning Driven Findings Uncover New Cellular Players in Melanoma Tumor Microenvironment Pointing to New Possible Strategies in Immunoptherapy
CytoReason / AACR
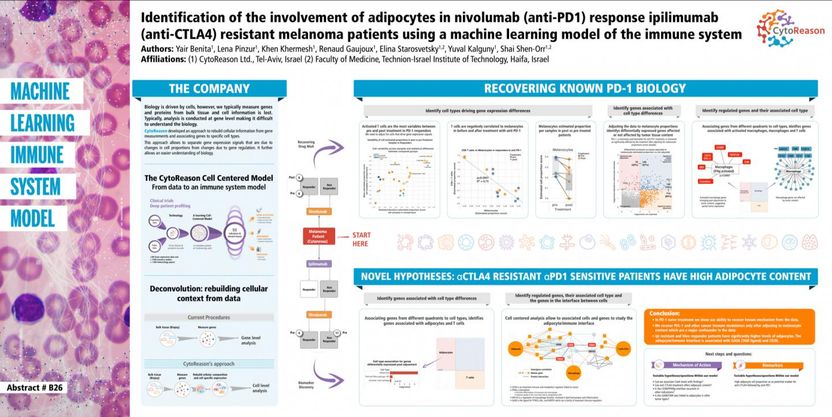
Analysis of data from melanoma biopsies, using CytoReason's proprietary machine learning-based approach, identified cells and genes that distinguish between nivolumab responders and non-responders in a cohort of ipilimumab resistant patients. The analysis revealed that adipocyte abundance is significantly higher in ipilimumab resistant nivolumab responders compared to non-responders (p-value = 2x10-7). It also revealed several undisclosed potential new targets that may be valuable in the quest for improved therapy in the future.
Adipocytes are known to be involved in regulating the tumor microenvironment. However, what these findings appear to show is that adipocytes may play a previously unreported regulatory role in the ipilimumab resistant nivolumab sensitive patient population, possibly differentiating nivolumab responders vs non-responders. It should be noted that these are preliminary findings based on a small sample of patients, and further work is needed to validate the results.
"The adipocyte finding was unexpected and raises many questions about the role of adipocytes in the tumor/immune response interface. It is currently unclear if adipocytes are affected by the treatment or vice versa, or represent a different tumor type", said Yair Benita, Head of Scientific Operations at CytoReason. "However, what we do know is that CytoReason's technology has put the spotlight on adipocytes, and the need to build a strategy to track them in future studies, so as to better understand their possible role in immunotherapy"
Gene expression analysis is a powerful tool in advancing our understanding of disease. However, approximately 90% of the specific pattern of cellular gene expression signature is driven by the cell composition of the sample. This obfuscates the expression profiling, making identification of the real culprits highly problematic.
CytoReason's platform works to overcome these issues. In this study, using a single published data set, CytoReason was able to apply its knowledge base and technologies to rebuild cellular composition and cell specific expression. This enabled CytoReason to undertake a cell level analysis, uncovering hidden cellular activity that was mapped back to specific genes that can be shown to emerge only when therapy is showing and effect.
"The immune system is predominantly cell-based. CytoReason is unique in that our disease models are specifically designed on a cellular level - replicating biology to crack key biological challenges, while learning from every data set", said David Harel, CEO, CytoReason. "CytoReason's computational platform integrates genetics, genomics, proteomics, cytometry and literature with machine learning to create our disease models. This analysis further demonstrates CytoReason's ability to generate novel hypotheses for new biological relationships that are often hidden to conventional methods - providing vital clues that are highly valuable in the drug discovery and development process."



























































