Advanced EEG analysis reveals the complex beauty of the sleeping brain
Advertisement
Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators have developed a novel approach to analyze brainwaves during sleep, which promises to give a more detailed and accurate depiction of neurophysiological changes than provided by a traditional sleep study. In a report published in the January issue of Physiology, the research team describes how applying a technique called multitaper spectral analysis to electroencephalogram (EEG) data provides objective, high-resolution depictions of brainwave activity during sleep that are more informative and easier to characterize than previous approaches. The researchers also present a visual atlas of brain activity during sleep in healthy individuals, highlighting new features of the sleep EEG - including a predictor of REM sleep - that could be of important use to clinicians and researchers.
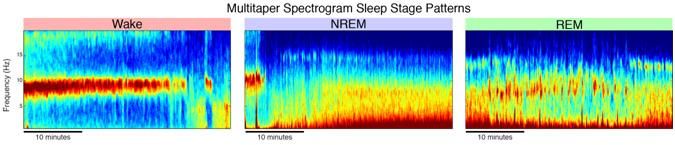
The sleep EEG multitaper spectrogram reveals patterns of continuous changes in brain oscillation activity during sleep. Characteristic patterns clearly differentiate waking (left) from nonREM (center) and REM sleep (left).
Michael Prerau, PhD
Clinical sleep analysis has historically centered on identifying and tracking common patterns of brain and physiological activity, called sleep stages. Identifying sleep stages has long been a time-consuming and subjective process. Starting in the late 1930s, sleep staging was performed using EEG machines that would cut a paper tape into sheets with 30-second traces of the patient's brainwave activity. A skilled technician would painstakingly take each paper sheet - almost 1,000 in an 8-hour sleep recording - and decide which sleep stage the patient was in by visual inspection of the EEG traces.
Almost 80 years later, other than slight refinement of the stages and the fact that the 30-second EEG traces now appear on a computer screen, the process of sleep staging remains virtually unchanged, remaining a time-consuming and fundamentally qualitative process. Consequently, even experienced scoring technicians still agree only 75 to 80 percent of the time. The progression of sleep stages over a night, called a hypnogram, is still used as the primary descriptor of sleep architecture. While the hypnogram has been an important tool for describing sleep architecture, since the numerous bumps and squiggles of brainwave traces become undiscernible by eye over large time scales, there are important drawbacks to relying on subjective summaries of sleep instead of objective data.
"During sleep, the brain is engaged in a symphony of activity involving the dynamic interplay of different cortical and sub-cortical networks," says Michael Prerau, PhD, of the MGH Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Management , lead author of the Physiology report. "Due to practical constraints and established practices, current clinical techniques greatly simplify the way the sleep is described, causing massive amounts of information to be lost. We therefore wanted to identify a more comprehensive way of characterizing brain activity during sleep that was easy to understand and quick to learn, yet mathematically principled and robust."
The approach used by the MGH investigators provides a paradigm shift allowing clinicians to move away from subjective sleep staging and harness the wealth of objective information contained within EEG data. In their report, the team describes how sleep oscillations are far more easily characterized using spectral estimation than by looking at EEG traces. Spectral analysis is a class of approaches that break a waveform signal into its component oscillations - repeating patterns over time- just as a prism breaks white light into its component colors. In the EEG, these oscillations represent the activity of specific brain networks during sleep and wakefulness.
"At a fundamental level, brain activity is truly organized in terms of oscillations and waves," says senior author Patrick Purdon, PhD, MGH Anesthesia. "Spectral analysis is just analyzing the signals in terms of these waves, making it the right tool - and in some ways the perfect tool - for the job." Purdon also points out that traditional sleep scoring is essentially a crude form of spectral analysis, based on recognizing the wave properties by eye.
Spectral analysis may not have been adopted for sleep scoring previously because the prevailing techniques for EEG spectral estimation produced noisy and inaccurate estimates of the power spectrum, making interpretation of the resulting spectrogram difficult. Consequently, the MGH team employed multitaper spectral analysis, a form with greatly reduced noise and increased accuracy compared to more basic methods. Computing a multitaper spectrogram of the sleep EEG, which tracks how the power and frequency of these oscillations change over time, provides more information about which networks are active at different points during sleep.
In their report the researchers use these new vivid images of brain activity to illustrate how the sleep EEG multitaper spectrogram objectively reveals the detailed architecture of an entire night of sleep in a single visualization, rather than 1,000 30-second windows. Repeating patterns of activity - which use color to reflect signal power - become apparent even to the untrained eye, allowing technicians with only a few hours of training to stage with an accuracy comparable to that of traditional sleep scoring.
The investigators comprehensively detailed an atlas of common patterns and transitions seen within healthy individuals during sleep and highlighted the ability of the sleep EEG multitaper spectrogram to show features on time scales ranging from many hours to microevents lasting a few seconds. They were also able to identify novel features of the sleep EEG, including a trend in which bursting in the low-frequency alpha range, which is not currently used in clinical sleep scoring, predicts the onset of REM sleep by several minutes. Purdon says, "We try to remind people that the sleep EEG isn't just a pile of 'big data.' In fact, it's highly structured, and that structure is deeply connected to the fundamental brain mechanisms of sleep."
Future research by the team will focus on developing robust quantitative metrics based on the spectrogram. "Moving forward, this enhanced approach will allow scientists to better characterize the complex heterogeneity observed in normal sleep and ultimately to assist in diagnosing sleep and related disorders," says Prerau, who has received a grant from the National Institute of Neurological Disease and Stroke to identify new disease biomarkers within sleep. "It is also fun and easy to learn!" Prerau has created the website http://sleepEEG. org , which hosts free, interactive tutorials designed to teach clinicians and investigators how to read the sleep multitaper spectrogram.
The researchers also are optimistic about the clinical applications of this method. Co-author Matt Bianchi, MD, PhD, of the MGH Department of Neurology and director of the MGH Sleep Lab, says, "The traditional hypnogram has not had the clinical application one might expect for such a fundamental aspect of sleep. This technique is poised to bring EEG patterns, a classic aspect of sleep medicine, back to the forefront. Overall, by improving physician review of patient data, these techniques hold promise to bring modern analytics to routine care - making the patterns of brain activity during sleep accessible and enabling physicians to see the EEG through this dynamic lens."