Stress bypasses quality control
Researchers find cellular mechanism to stop quality control of gene expression
Advertisement
Under stressful life conditions many proteins lose their functionality. A natural mechanism that can be found in all cells leads to the preferred synthesis of stabilizing proteins (so called chaperones), which protect cells from stress and the subsequent “destruction” of normal proteins. Scientists from the University of Göttingen have addressed the question of how this life-saving mechanism works.
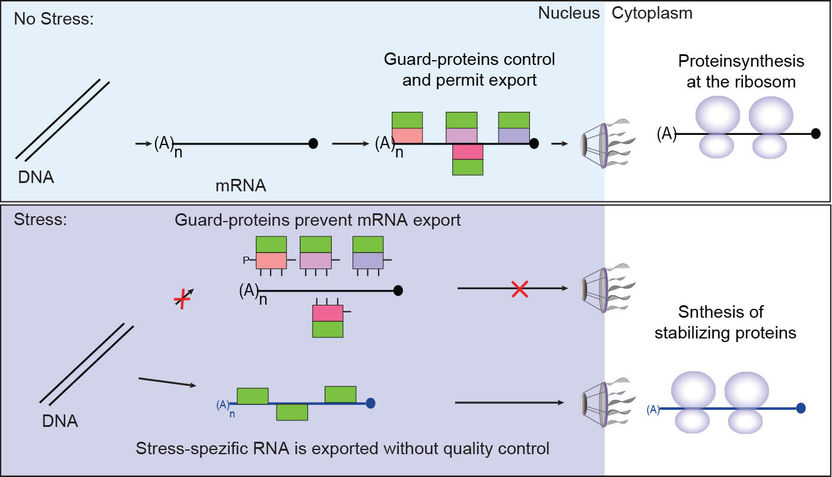
The team of Professor Heike Krebber, head of the study and Director of the Department of Molecular Genetics, found out that the synthesis of regular proteins always involves quality control steps during the synthesis of the mRNA (messenger RNA) and prior to its nuclear export into the cytoplasm in which the mRNAs are translated into proteins by large protein factories, the ribosomes. These quality control mechanisms are prevented during stress. Thus, the cell rather accepts false mRNAs than undergoing cell death.
Under normal conditions, regular mRNAs are synthesised as precursor-mRNAs, which require several maturation steps. Every step is surveyed by a group of guarding adapter proteins (guardian proteins) that bind to the RNA and check them for correctness. The processing of the pre-mRNA to the mature mRNA also includes the excision of intron sequences, large regions that do not encode proteins and that would interrupt and disturb the mRNA translation into proteins. Mistakes during maturation are detected by the guard-proteins that recruit an RNA-degradation machinery (the TRAMP-complex and the nuclear exosome), which remove the false mRNAs from the cell. Instead, when processing occurs correctly, the guardian proteins recruit an mRNA export receptor (Mex67-Mtr2), which resembles a bus ticket for nuclear export and allows passage of the mature and controlled mRNA through the nuclear pore complex into the cytoplasm. The correct mRNAs can now be reached by the translation machinery and translated into correct proteins. This mechanism is important to prevent the translation of e.g. intron containing mRNAs, which can be toxic to the cell and harmful for an organism, as this can lead to diseases like cancer or neurodegenerative diseases.
The Göttingen researchers discovered that during cellular stress, normal mRNAs are not transported into the cytoplasm and not translated anymore. This is accomplished by dissociation of the guardian proteins with the export receptor from the mRNAs in the nucleus. In response to stress, cells synthesise specific stress-responsive transcripts that encode for stabilizing chaperone proteins that help the cell to survive the devastating situation. “The exciting thing is”, Professor Krebber says, “that these stress specific mRNAs are not quality controlled and they are sent to the cytoplasm without the usual control of the guard-proteins, which speeds up the synthesis of the proteins required under cellular stress and which simply enables survival under stress.”
This mechanism of the guardian protein independent mRNA export is triggered by the gene promoter, by which transcription is initiated. This becomes clear from experiments in which a normal gene can be converted into a gene that is expressed during stress by exchanging its promoter. This engineered RNA leaves the nucleus during stress without quality control. This mechanism allows cells to survive a stressful situation for a longer time, which is important for the basic understanding of the functioning of a cell and provides knowledge for therapies. In particular the lacking quality control in stressed cells is an interesting fact that needs further research.
Scheme to the study
Prof. Dr. Heike Krebber, Universität Göttingen























































