Researchers uncover protein-based “cancer signature”
A research team at the University of Basel’s Biozentrum has investigated the Expression of ribosomal proteins in a wide range of human tissues including tumors and discovered a cancer type specific signature. As the researchers report in “Genome Biology” this “cancer signature” could potentially be used to predict the progression of the disease.
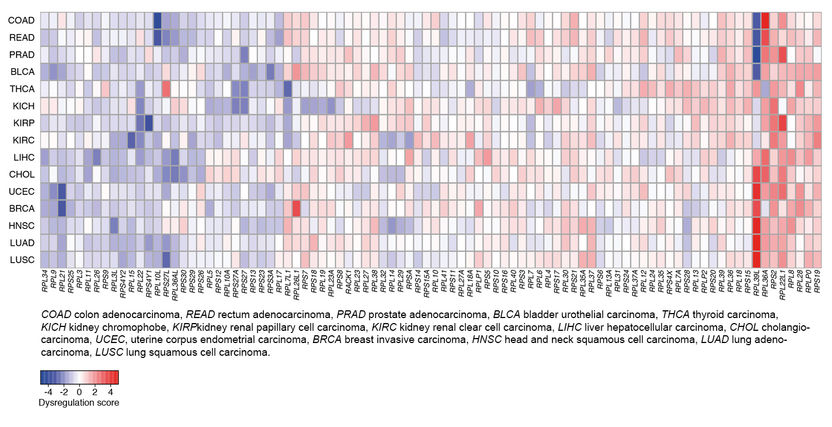
Gene expression level of individual ribosomal proteins (RP) in different types of cancer (blue: lower level; red: higher level compared to normal tissue).
University of Basel, Biozentrum
Proteins are the building blocks of life. They are produced by molecular machines, called ribosomes. A human ribosome contains some eighty ribosomal proteins. Prof. Mihaela Zavolan’s research group at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel has now discovered that about a quarter of the ribosomal proteins have tissue-specific expression and that different cancer types have their own individual expression pattern of ribosomal proteins. In the future, these patterns may serve as a prognostic marker for cancer and may point towards new therapeutic opportunities.
Cellular machines for protein synthesis
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis and are thus essential for the cell. Therefore, it has long been assumed that the expression of the individual components of the ribosomes is strictly controlled and invariant. A few studies, however, have already suggested that the expression of individual ribosomal proteins is altered in cancers as well as in diseases of the hematopoietic system such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
“Cancer signature” revealed by systematic data analysis
Mihaela Zavolan and her co-worker Joao Guimaraes have systematically analyzed ribosomal protein expression in thirty tissue types, three hundred different cell types and sixteen different types of tumors, such as lung and breast cancer. In contrast to previous assumptions, they found a wide variability in ribosomal protein gene expression. In particular, hematopoietic and tumor cells display the most complex expression pattern.
“For us, it was really impressive to see that consistent signatures emerged for the different cancer types after the analysis of distinct data sets including patient samples,” explains first author Guimaraes. “The pattern of the dysregulated proteins is very striking, whereby the expression of some ribosomal proteins is systematically reduced, and of others increased in cancer cells. This suggests that individual ribosomal proteins can either suppress or promote tumorigenesis.”
Expression pattern as a prognostic marker
Furthermore, the scientists discovered a strong relationship between the “signature” in breast cancer and the relapse-free survival. “We were quite surprised to find that the expression level of just three ribosomal proteins allows a fairly accurate prognosis of disease progression, comparable to the best predictive markers that are currently known”, Zavolan points out.
“Our study demonstrates the potential of such expression signatures for the prognosis and perhaps a diagnosis of cancer. We are especially interested to study the functions of individual ribosomal proteins and hopefully open the door for new therapeutic options,” explains the scientist.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
BioMed X and Boehringer Ingelheim start new joint research group
Nobilon advances first vaccine into human trials - Intranasal influenza vaccine begins Phase I clinical development
Raptor Pharmaceuticals and TorreyPines Therapeutics Receive Stockholder Approvals to Merge - Merger to Create NASDAQ-Listed Biopharmaceutical Company named Raptor Pharmaceutical Corp.
Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine 2020 Announced - Nobel Prize awarded to Harvey J. Alter, Michael Houghton and Charles M. Rice for the discovery of Hepatitis C virus
PharmAthene and SIGA Technologies sign definitive merger agreement
PerkinElmer announces third quarter results - GAAP Revenue of $548 million versus $563 million in the comparable prior period

Glox Therapeutics Secures £4.3M Seed Funding to Develop Precision Antimicrobials Targeting Drug-resistant Bacteria - Spin-out from the Universities of Glasgow and Oxford

Doped by food - Dopamine release regulates our eating behaviour

Turning fallen leaves into sustainably made paper - Ukrainian scientist selected as a finalist for the Young Inventors Prize 2024
Merck Celebrates Topping-Out Ceremony for New Membrane Production Plant - Investment of more than € 140 million creates approximately 55 new jobs






















































