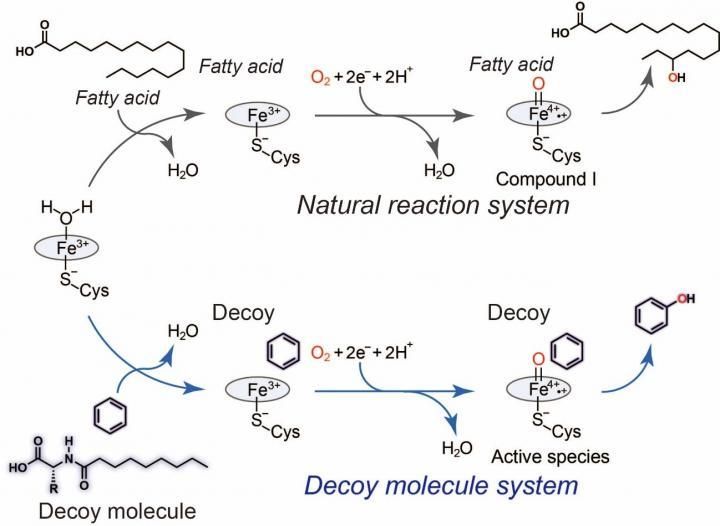
A new regulator in glucose metabolism
diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease that has become increasingly prevalent in the population: More than six million people are affected by the disease alone in Germany. It is characterized by a disruption of the glucose metabolism and (except for type 1 diabetes) an impaired response of the body to the hormone insulin. Scientists are currently seeking to find the cause and possible regulators of the disease in order to intervene therapeutically.
Immunofluorescence microscopy of TSC22D4 (red) expressing cells.
Helmholtz Zentrum München
A team led by the metabolism expert Professor Stephan Herzig, director of the Institute for Diabetes and Cancer at Helmholtz Zentrum München (IDC), has discovered a new mechanism that is responsible for the regulation of the glucose metabolism. The transforming growth factor beta 1-stimulated clone 22 D4, abbreviated TSC22D4, acts as a molecular switch in the liver and from there regulates genes that can influence the metabolism throughout the body.
Approach from Cancer Research
"The current study is a successful continuation of our research activities with colleagues from the Internal Medicine at Heidelberg University Hospital," said study leader Herzig, who left Heidelberg in 2015 to become director of the Institute for Diabetes and Cancer at Helmholtz Zentrum München. Already in 2013 the researchers showed that increased production of TSC22D4 in the liver of mice with cancer leads to severe weight loss (cachexia) . In the present study, they investigated the role of this gene regulator in connection with diabetes.
"The strong influence of TSC22D4 on the metabolism in tumor diseases suggested that it could also play a role in metabolic diseases," said first author Dr. Bilgen Ekim Üstünel of the IDC. In the current study, the researchers showed in diabetic mice that inactivation of TSC22D4 led to an improvement of the insulin action and glucose metabolism. Further analyses revealed that TSC22D4 in particular inhibits the production of the lipocalin13 protein, which is released as a messenger substance from the liver and can regulate the glucose metabolism in other organs.
To check the relevance of the new mechanism in the clinic, the researchers examined liver tissue specimens of 66 patients with and without type 2 diabetes. They found that in the liver of the diabetes patients compared to people with normal glucose metabolism, the TSC22D4 gene was expressed significantly more often and lipocalin13 was produced correspondingly less often. "For the treatment of diabetes there is only a very limited number of therapeutic targets," said Herzig. "Next, we want to investigate whether our findings can lead to the development of a new therapeutic approach to treat diabetes and insulin resistance."
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents

Microrobots for the study of cells - Opportunities for cancer treatment and wound healing