New computational tool may speed drug discovery
A new computational tool called fABMACS is helping scientists see beyond static images of proteins to more efficiently understand how these molecules function, which could ultimately speed up the drug discovery process.
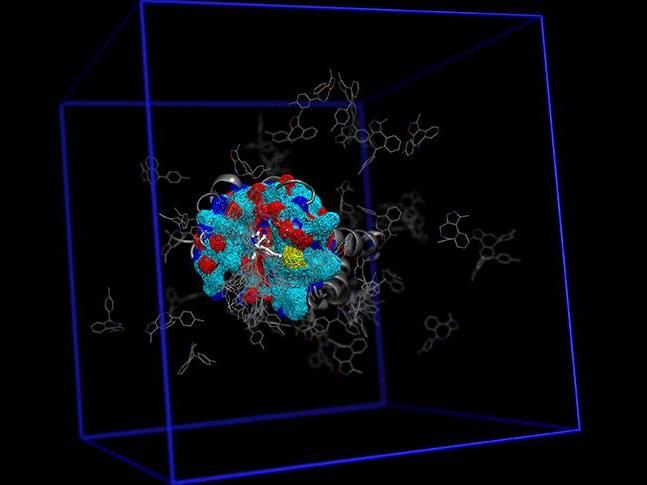
Simulation of BRD4 interacting with a potent inhibitor.
Image courtesy of Dr. Bradley Dickson, Rothbart Laboratory, Van Andel Research Institute.
Proteins are the molecular workhorses of biology--they carry out the instructions written in the genetic code. Their shape plays a crucial role in their function and their ability to interact with other molecules. Scientists study these interactions to develop new insights into protein function and to develop targeted therapies for diseases such as cancer.
"The goal of targeted drug design is to create a molecule that interacts specifically with a protein, and this requires a description of protein-drug interactions that is precise--down to the placement of each atom," said Bradley Dickson, Ph.D. , a computational biophysicist in the laboratory of Scott Rothbart, Ph.D. , at Van Andel Research Institute (VARI) and first author of a paper describing the tool. "The creation of fABMACS is a significant step toward robust virtual drug discovery because it saves time and money. It allows us to better harness the power of existing software while greatly improving our ability to predict the way that a potential drug interacts with a protein."
Scientists often rely on collecting snapshots of proteins to determine how they may interact with a potential drug. However, these images are static and do not depict changes in proteins' shape.
"These snapshots provide valuable insight that can be enriched by fABMACS," said Rothbart, assistant professor at VARI and the study's senior author. "fABMACS allows us to simulate chemical changes to the drug and more quickly predict how those changes impact its interaction with the target protein. Ultimately, this could translate to improved drug potency and efficacy."
To demonstrate the tool's capabilities, the team ran several accelerated computer simulations of the epigenetic regulatory protein BRD4 bound to a drug that is currently in phase I clinical trials for blood cancers. They demonstrated that a slight change to the compound's chemical structure could improve binding to its target protein, thereby improving its effect.
Fast, stable and scalable
fABMACS is an add-on to existing molecular dynamics software. It is based on GROMACSv5.0.5 and optimizes network communication and load balancing--both critical aspects of software development in parallel computing environments--to achieve a low-overhead implementation of new free-energy techniques. fABMACS also comes with a built-in configuration tool that allows the code to be tailored to different applications without requiring the user to manually edit the code, which maximizes transferability.
Original publication
Most read news
Original publication
Dickson, Bradley M. and de Waal, Parker W. and Ramjan, Zachary H. and Xu, H. Eric and Rothbart, Scott B.; "A fast, open source implementation of adaptive biasing potentials uncovers a ligand design strategy for the chromatin regulator BRD4"; J of Chemical Physics; 2016
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Dentistry_throughout_the_world
Carol_Cass
Charcot-Marie-Tooth_disease
John_Dick_(scientist)
Gamblers_Anonymous
AMP-activated_protein_kinase
Antoine_Prioré
Edward_Blyth