Artificial enzyme for asymmetric synthesis using a synthetic chiral polymer
enzymes, high-molecular-weight chiral polymeric compounds, are complex biological catalysts. Capture of the substrate molecule, catalyzing the reaction, and release of the product are three important events performed by enzymes. In order to accomplish these important events using a synthetic catalyst, the catalyst must necessarily have a large molecular weight so that it can act as a highly specific catalyst. However, synthetic chiral polymers for this purpose have not been designed so far. A research team in the Department of Environmental and Life Science at Toyohashi University of Technology has investigated a novel synthetic method for preparing chiral polymers containing repeating units of cinchona sulfonamide.
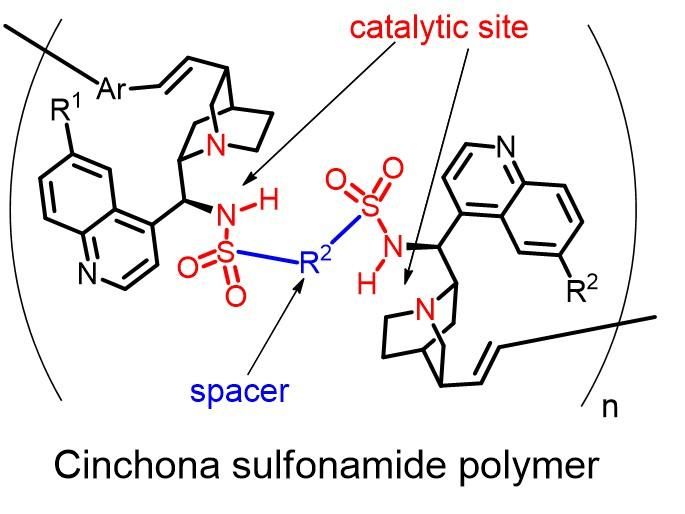
This is the structure of cinchona sulfonamide polymer.
Copyright (C) Toyohashi University Of Technology. All rights reserved.
The lead author Shohei Takata said, "After testing many reaction conditions for the polymerization, we have synthesized chiral polymers containing cinchona sulfonamide repeating units. Chiral polymers are easily prepared by the method we established."
"We have found that Mizoroki-Heck coupling was successful in synthesizing cinchona sulfonamide polymers," explains the leader of the research team, Professor Shinichi Itsuno, "Moreover, our chiral polymers showed high catalytic activity in asymmetric reactions." Various kinds of such chiral polymers may be synthesized using this newly developed methodology to obtain various types of synthetic enzymes for specific reactions.
Furthermore, the chiral polymers developed in this study are insoluble in the usual organic solvents or water. The insoluble polymeric catalysts can be packed into a column, into which the substrate compounds can be introduced. The desired product can then be continuously obtained from the column. Without a usual reaction vessel, a continuous flow system may be possible using the polymeric catalyst. The flow system is a necessary technology for the automation of fine chemical syntheses.
Original publication
Most read news
Original publication
Takata, Shohei and Endo, Yuta and Shahid Ullah, Mohammad and Itsuno, Shinichi; "Synthesis of cinchona alkaloid sulfonamide polymers as sustainable catalysts for the enantioselective desymmetrization of cyclic anhydrides"; RSC Advances; 2016
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Caspase
Cyclooxygenase

Machine learning classifier accelerates the development of cellular immunotherapies - "To finance further development, we have founded the biotech start-up Tcelltech"
AIR_(program)
Streptococcus_pneumoniae
Building a better botox - Small engineering tweaks to botulinum toxin B could make it more effective and longer-lasting with fewer side effects

Optimizing Kinetics Assays to Prevent Avidity Effects - Robust experimental design avoids artefacts in the measurement of binding kinetics and affinity
Alpha-Ethyltryptamine
Olink Genomics expands: New location and recruitment of CTO
People with MS-related memory and attention problems have signs of extensive brain damage