Using nature's own solvents for the preparation of pure lignin
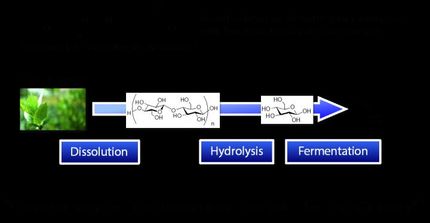
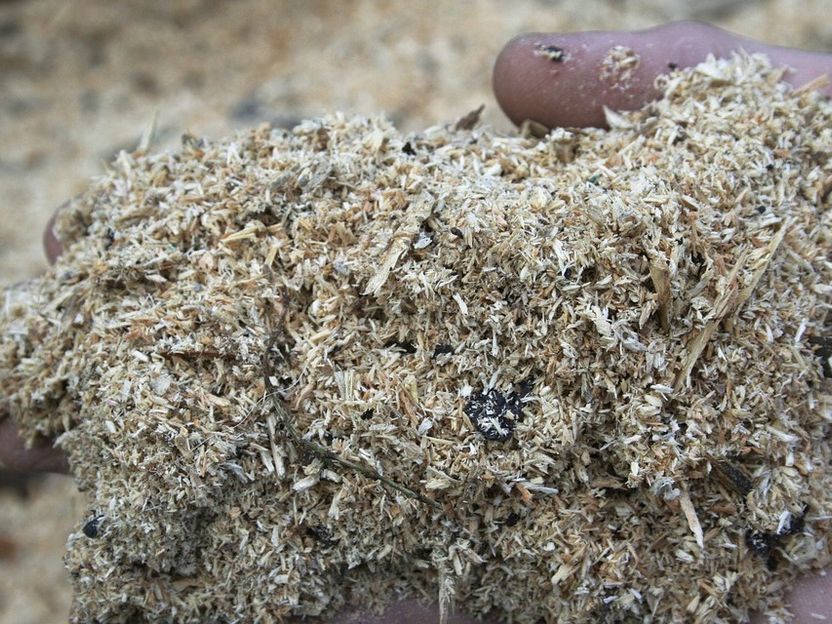
Lignin can now be efficiently and cost-effectively separated from sawdust, by using eutectic solvents. VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland has developed solvents using which 50% of the lignin from wood can be extracted in a pure form that retains its natural chemical structure during processing. Using eutectic solvents, it may be possible to produce materials for use in the forest, food processing, pharmaceutical, packaging and mining industries in the future.

disign; pixabay.com; CC0
The use of eutectic solvents presents a range of opportunities for using lignin in industrial applications. A VTT research programme aims to replace petroleum-based chemicals with cost-effective, environmentally friendly alternatives in forest, pharmaceutical and mining industry applications; these will provide Finnish companies with a competitive edge on the international markets.
One of the key results of the research is the separation of lignin from sawdust in such a manner that up to 100% of the lignin maintains its natural chemical structure. Conventional processes provide lignin in a form which is much less usable in terms of its chemistry. This is why lignin has mainly been used for combustion in energy production. Lignin which has retained its natural organic structure is thought to be more reactive and homogeneous, and therefore easier to use in various applications.
VTT's research is also opening up new opportunities to use enzymes in fractionation and metabolising processes – according to the preliminary results, carbohydrate-metabolising enzymes can maintain their stability surprisingly well in certain DES solvents, whereas enzymes have tended to be relatively unstable in new biomass-degrading solvents, such as ionic liquids, which resemble DES solvents in many of their properties.
Some components of eutectic solvents are fit for consumption. Interactions between the components enable chemical reactions that would be impossible to create with conventional chemical processes.
Eutectic solvents are prepared simply by heating and stirring and are inexpensive compared to conventional ionic solvents. However, their recoverability and recyclability via industrial processes have to be investigated in each case.
VTT is studying eutectic solvents as part of the 'Oil-free chemistry programme' funded by Tekes, which ended in the spring of 2016. The results indicate that eutectic solvents can be utilised in applications such as biomass fractionation, the stabilisation of certain enzymes, and potential new surface-active agents.
Original publication
Wahlstrom, Ronny and Hiltunen, Jaakko and Pitaluga de Souza Nascente Sirkka, Mariah and Vuoti, Sauli and Kruus, Kristiina; "Comparison of three deep eutectic solvents and 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate in the pretreatment of lignocellulose: effect on enzyme stability, lignocellulose digestibility and one-pot hydrolysis"; RSC Adv.; 2016
Jaakko Hiltunen, Lauri Kuutti, Stella Rovio, Eini Puhakka, Tommi Virtanen, Taina Ohra-Aho & Sauli Vuoti; "Using a low melting solvent mixture to extract value from wood biomass"; Scientific Reports; 2016