Viral-based therapy for bone cancer
Scientists at Okayama University develop a viral-based technique specific to bone cancer that enhances patients’ sensitivity to chemotherapy.
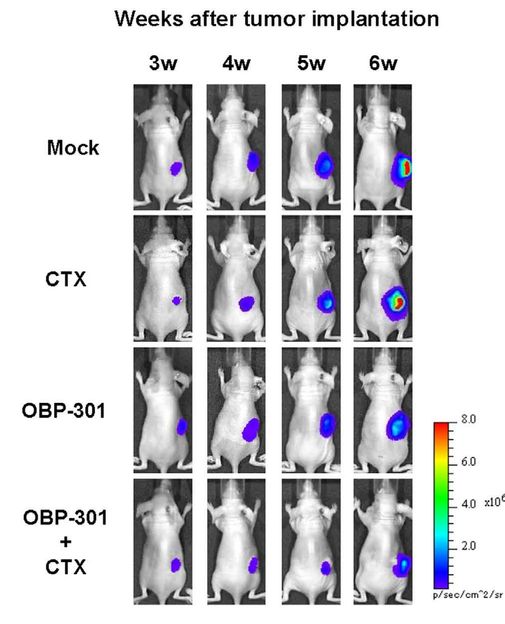
Researchers at Okayama University have developed a combined therapy (OBP-301 plus CTX in image) using an adenovirus and chemotherapy agents to induce chemo-sensitivity in bone cancer tumors. Their success could transform treatment for bone cancer sufferers and other chemo-resistant forms of cancer in future.
Okayama University
Certain cancers, including osteosarcoma (bone cancer), are unresponsive to chemotherapy, making disease prognosis very poor. Osteosarcoma is a rare but severe form of cancer that predominantly affects the growing bones in children and adolescents. The cancerous tissue in osteosarcoma is resistant to chemotherapy, but the precise molecular mechanisms involved are unclear. The search is on to find a way of enhancing the chemo-sensitivity of patients, so that they are more responsive to treatment.
Now, Toshiyoshi Fujiwara and co-workers at Okayama University, Japan, have developed a new combined therapy which uses the properties of a virus to disrupt osteosarcoma cancer cells and enable chemotherapy agents to destroy them. Their findings may transform treatment of bone cancer and other chemo-resistant cancers in future.
One possible target for improving chemo-sensitivity is the BCL2 protein family; these proteins are overexpressed in cancer tissues and aid in the progression of the disease. One such protein is MCL1, whose role is to limit cancer cell death in tumors. The researchers focused on finding a way of downregulating MCL1 in osteosarcoma in the hope that it might encourage chemo-sensitivity.
To do this, Fujiwara’s team used their newly-engineered ‘telomerase-specific ocolytic adenovirus OBP-301 (telomelysin)’, which they had previously shown could reduce the growth of stomach tumors. They created a combined therapy using OBP-301 with chemotherapy agents. The researchers found that OBP-301 activated microRNA-29, which in turn worked to downregulate MCL1. MCL1 knockdown resulted in high levels of cancer cell death in osteosarcoma tumors, weakening the tumors and leaving them open to the effects of chemotherapy.
Original publication
Shuhei Osaki, Hiroshi Tazawa, Joe Hasei, Yasuaki Yamakawa, Toshinori Omori, Kazuhisa Sugiu, Tadashi Komatsubara, Tomohiro Fujiwara, Tsuyoshi Sasaki, Toshiyuki Kunisada, Aki Yoshida, Yasuo Urata, Shunsuke Kagawa, Toshifumi Ozaki & Toshiyoshi Fujiwara; "Ablation of MCL1 expression by virally induced microRNA-29 reverses chemoresistance in human osteosarcomas"; Scientific Reports; 2016
Original publication
Shuhei Osaki, Hiroshi Tazawa, Joe Hasei, Yasuaki Yamakawa, Toshinori Omori, Kazuhisa Sugiu, Tadashi Komatsubara, Tomohiro Fujiwara, Tsuyoshi Sasaki, Toshiyuki Kunisada, Aki Yoshida, Yasuo Urata, Shunsuke Kagawa, Toshifumi Ozaki & Toshiyoshi Fujiwara; "Ablation of MCL1 expression by virally induced microRNA-29 reverses chemoresistance in human osteosarcomas"; Scientific Reports; 2016
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.