A new molecular player involved in T cell activation
Advertisement
When bacteria or viruses enter the body, proteins on their surfaces are recognized and processed to activate T cells, white blood cells with critical roles in fighting infections. During T-cell activation, a molecular complex known as the microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) moves to a central location on the surface of the T-cell. microtubules have several important functions, including determining cell shape and cell division. Thus, MTOC repositioning plays a critical role in the immune response initiated by activated T cells.
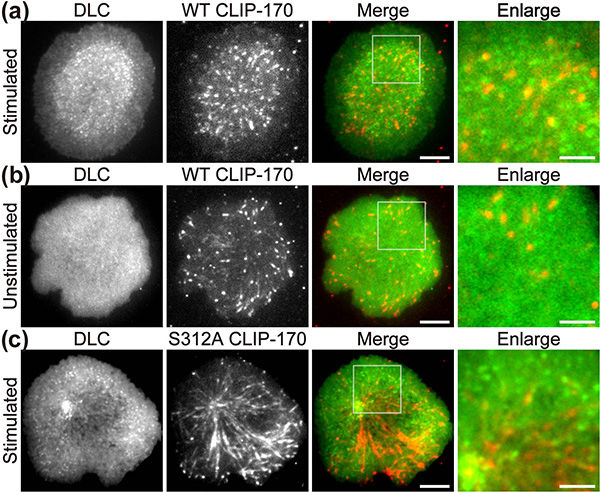
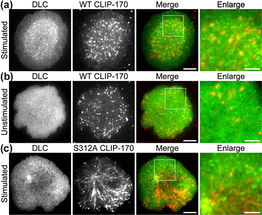
Fluorescence live-cell imaging of the wild-type CLIP-170-TagRFP-T (a,b) or a phosphodeficient S312A mutant CLIP-170-TagREP-T (c) and dynein light chain (DLC)-mEGFP co-expressed in T cells. Increased dynein relocation to the center, which is responsible for MTOC repositioning, requires both stimulation and CLIP-170 phosphorylation. The boxed regions in the merged images are enlarged (right). Scale bars: 5 μm (left, 2nd left, merged) and 2 μm (right)
Tokyo Tech
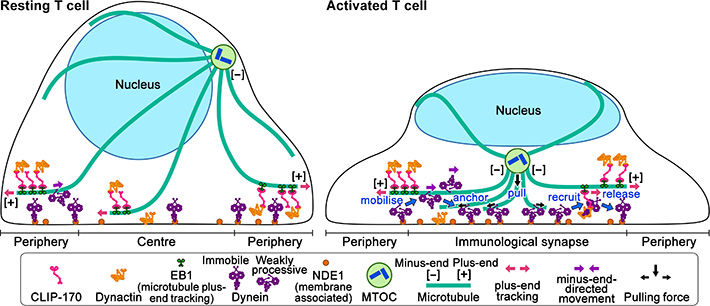
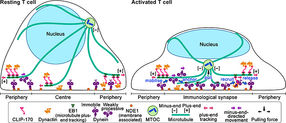
In resting T cells, the majority of dynein is immobile on the contacted cell surface and is located at the periphery region. T cell stimulation increases the fraction of dynein undergoing minus-end-directed motility (“mobilise”), which is a “weakly processive” state. Then, the dynein is anchored to the surface (“anchor”). Alongside this, stimulation induces some fraction of dynein to colocalize with CLIP-170 and dynactin and follow plus-end tracking (“recruit”). After tracking of one or two micrometers, the dynein is released from the complex and anchored (“release”). As a result, dynein relocation increases to the center region of the contact surface, the immunological synapse, where “anchored” dynein molecules are immobile and or weakly processive at a velocity in good agreement with the velocity of MTOC repositioning. “Anchored” and weakly processive dynein pulls the microtubules and the MTOC (“pull”), which causes MTOC repositioning near the immunological synapse and full activation of T cells. Phosphorylation of CLIP-170 is essential for dynein recruitment to the plus-end and for dynein relocation.
Tokyo Tech
Lim Wei Ming and Yuma Ito, along with their colleagues at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), provide compelling evidence that a key protein responsible for the relocation of the MTOC in activated T cells is a molecule known as CLIP-170, a microtubule-binding protein.
The researchers used live-cell imaging to uncover the mechanism of MTOC relocation. “The use of dual-color fluorescence microscopic imaging of live T cells allowed us to visualize and quantify the molecular interactions and dynamics of proteins during MTOC repositioning,” notes Dr. Sakata-Sogawa. This technique allowed them to confirm that phosphorylation of CLIP-170 is involved in movement of the MTOC to the center of the contacted cell surface; the findings were confirmed using both cells with phosphodeficient CLIP-170 mutant and cells in which AMPK, the molecule that phosphorylates and activates CLIP-170, was impaired. Further imaging showed that CLIP-170 is essential for directing dynein, a motor protein, to the plus ends of microtubules and for anchoring dynein in the center of the cell surface. Dynein then pulls on the microtubules to reposition the MTOC to its new location in the center.
“These findings shed new light on microtubule binding proteins and microtubule dynamics,” explains Dr. Tokunaga. Such research is critical, as a deeper understanding of T cell activation in the immune response, and could lead to the development of safer methods for cancer immunotherapy because presentation of CTLA-4, which is found by a 2018 Nobel Prize laureate and used as a target of the therapy, is also regulated by MTOC repositioning.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Cell Analysis
Cell analyse advanced method allows us to explore and understand cells in their many facets. From single cell analysis to flow cytometry and imaging technology, cell analysis provides us with valuable insights into the structure, function and interaction of cells. Whether in medicine, biological research or pharmacology, cell analysis is revolutionizing our understanding of disease, development and treatment options.

Topic World Cell Analysis
Cell analyse advanced method allows us to explore and understand cells in their many facets. From single cell analysis to flow cytometry and imaging technology, cell analysis provides us with valuable insights into the structure, function and interaction of cells. Whether in medicine, biological research or pharmacology, cell analysis is revolutionizing our understanding of disease, development and treatment options.