Computer simulation renders transient protein structures visible
Chemists at the University of Basel have succeeded in using computer simulations to elucidate transient structures in proteins. The researchers set out how computer simulations of details at the atomic level can be used to understand proteins’ modes of action.
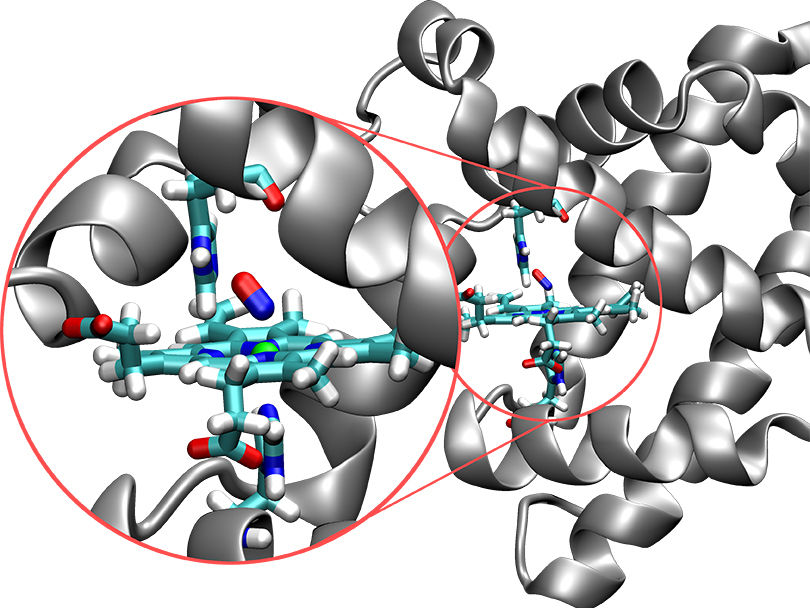
Structure of the protein myoglobin (silver) with the embedded active site (in color). In this image, the nitrogen molecule (red/blue) is bonded to the iron atom (green ball).
Universität Basel, Departement Chemie
Using computational chemistry, it is possible to characterize the motion of individual atoms of a molecule. Today, the latest simulation techniques allow scientists to quantitatively describe the dynamics of molecules and systems containing hundreds of thousands of atoms. These techniques are important, above all, for characterizing molecular states that are difficult to observe directly in experiments due to their short lifetime. Here, computer simulations are a source of valuable complementary insight.
A protein’s function is determined by its structure and dynamics. It is particularly important that information relevant to the nature of structures and molecular processes in the active site – i.e. the place where chemical reactions take place – is known. The formation and breaking of chemical bonds is a dynamic process that results in structural changes. The observable dynamics usually result in stable (low energy) states that are reached via one or more metastable (higher energy) intermediate steps. Whether a metastable state can be detected directly in an experiment depends on its lifetime. If it is too short, only indirect detection methods are available.
Computer determines atomic geometry
Now, a research team led by Prof. Markus Meuwly from the Department of Chemistry at the University of Basel has used molecular dynamics simulations to characterize the spatial and temporal behavior of the protein myoglobin. Myoglobin plays an important role in the transport of oxygen within cells and is found mainly in muscle tissue. Nitrogen monoxide, which is formed in the cells, is a short-lived and reactive messenger that is important in regulating vasodilation under hypoxia.
“The process by which nitrogen monoxide binds to myoglobin is already well characterized experimentally, which is important for the calibration of computer simulations,” explains Meuwly. “There is also experimental evidence for the existence of metastable intermediates, but our simulations provide insights into the underlying chemical structure and the dynamics of these intermediates, and thus the function of the protein.
Together with experimental observations, therefore, computer simulations are the basis for an understanding of complex chemical and biological systems. Accordingly, this combined approach also provides a starting point for further questions to be addressed; for example, the adaptation and optimization of proteins or active pharmaceutical agents. This requires an understanding of the underlying processes at the molecular and atomic level.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Tooth_development
Dynamic_light_scattering
Victorian_Students'_Aid_Program_(VSAP)
Curvibacter
MemoryArchive
Quaternary_structure
Forgetting uses more brain power than remembering
Fernand_Labrie
Concurrent_overlap