Mother’s intestinal microbes strengthen newborn babies
Mother’s intestinal microbes prepare her baby for life outside the womb. Swiss scientists found out how it works.
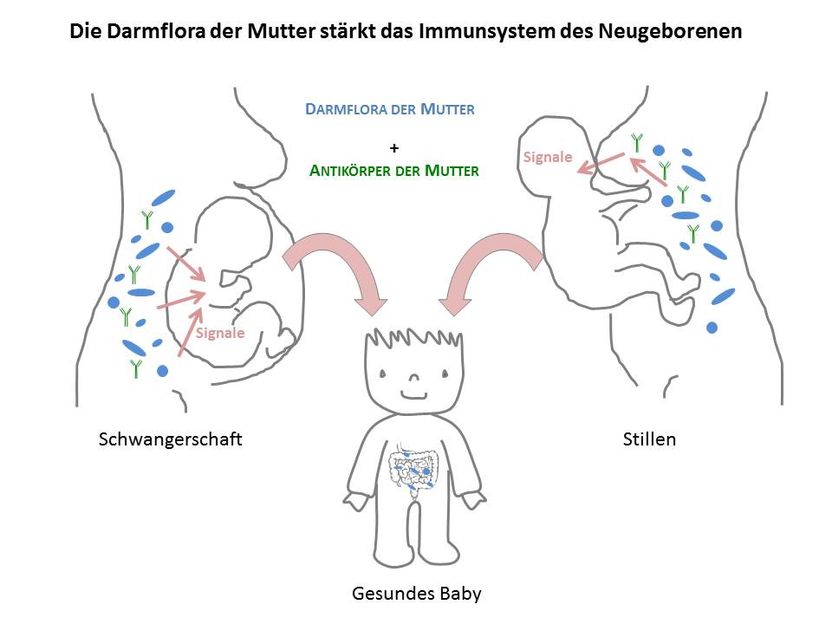
Tiny fragments of the mother’s intestinal microbes are passed to the baby across the placenta in the womb or in the mother’s milk during nursing.
Inselspital, Bern University Hospital
The birth of a newborn baby is the ultimate life-event. Babies leave the sterile and sheltered environment of the womb and enter a world teeming with bacteria. After birth all body surfaces get progressively colonized with microbes and within days the intestine becomes inhabited with ten-times more bacteria than there are cells of the baby’s own body.
Fortunately, newborn babies normally survive this sudden tsunami of incoming microbes without problems. We may take this for granted, but there are 6 million deaths each year worldwide in children under the age of 5, many of which are caused by intestinal infections and malnutrition. The big problem after birth is that the intestine must become colonized by microbes without allowing body tissues to become infected or damaging the ability of the intestine to absorb nutrients.
It has long been known that breast feeding by the mother provides nutrients and antibodies that help to protect her baby from infections. Yet even with this nursing from the mother, the baby’s immune system is very immature and sensitive to damage. Until now, the newborn body was thought only to begin the main process of adapting to so many intestinal bacteria after birth.
Work by researchers at the University Clinic for Visceral Surgery and Medicine at the Bern University Hospital, Switzerland, now published in Science, has modelled how this happens in mice. Their work shows that the baby is in fact prepared for the process of microbial colonization after birth by the microbes of the mother’s own intestines.
Tiny fragments (molecules) of the mother’s intestinal microbes enter her body and are passed to the baby across the placenta in the womb or in the mother’s milk during nursing. These fragments are too small to cause an infection themselves, but they stimulate cells in the baby to prepare its immune system and its intestine for the moment after birth when the baby has to deal with live intestinal bacteria on its own.
“We have always known that we may thank our mothers for their love and protection, now we also know that we must be grateful to their intestinal microbes”, says Andrew Macpherson, Full Professor of Medicine at the University of Berne and Director of Gastroenterology at the Bern University Hospital.
Most read news
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.





















































