A cheap, disposable device for diagnosing disease
The development of a reusable microfluidic device for sorting and manipulating cells and other micro/nano meter scale objects will make biomedical diagnosis of diseases cheaper and more convenient in regions where medical facilities are sparse or cost is prohibitive. Researchers at Penn State have recently filed a patent to develop such a device.
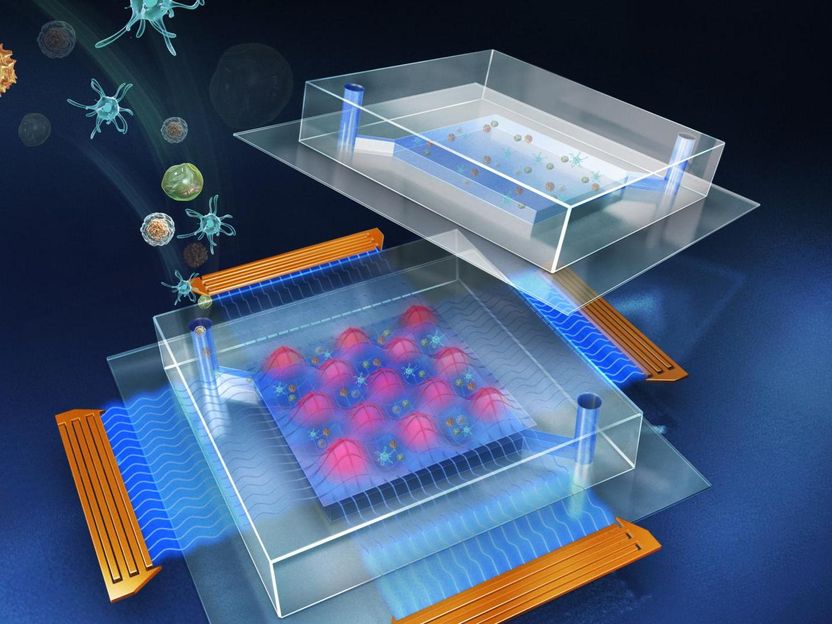
The cover image of the current issue of the journal Lab on a Chip shows an artist's conception of a reusable acoustic tweezers device (bottom) with a disposable microfluidic laboratory for cell manipulation and disease diagnosis.
Huang Lab/Penn State
Based on gentle acoustic vibrations, the device, called acoustic tweezers, is the work of Penn State professor of engineering science and mechanics , Tony Huang and his students.
"We believe our acoustic tweezers have tremendous potential, especially in diagnostics, with some applications also in therapeutics," Huang said. "Our current device works well, but to be used in diagnostics, the whole device has to be disposed of after one use. We have now found a way to separate the fluid-containing part of the device from the much more expensive ultrasound-producing piezoelectric substrate. This makes disposable acoustic tweezers possible."
Huang believes that the disposable plastic portion of the device can be manufactured for as little as 25 cents per unit. Even with the addition of electronics for diagnosis, which could be easily added off the shelf, he foresees a manufacturing cost of a few dollars for the complete permanent system, which could then be used over and over with the simple replacement of the plastic microfluidic channels.
"We want to push this toward a commercial product, something that can help people and benefit society," Huang said.
In the prior device, the microfluidic channel was permanently bound to the substrate and the ultrasound would be radiated directly into the fluid. In the new device, there is an intervening layer, but the ultrasound force is strong enough to manipulate the cells and to pattern them. This patterning of cells is especially important in studying cell-to-cell communication in biology labs or for drug screening.
"In drug screening, you want to examine how cells respond to drugs. With our acoustic tweezers, we can create a high throughput of single cells and see how they respond to drugs. Or, we create all types of cell assemblies and see how they respond to drugs, much more like how it would work inside the body," said Feng Guo, a Ph.D. student in Huang's group and lead author of the paper "Reusable acoustic tweezers for disposable devices."
In addition to its use in diagnosing diseases such as HIV and tuberculosis, both of which are endemic in resource-poor regions of the world, the device should find widespread use in hospitals, clinics, biology labs and the home due to its low cost and ease of use.
Original publication
Most read news
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Genetic causes of canine mammary tumors
Evolva reaches milestone in BASF collaboration
MedGenome secures series C funding

Evotec initiates ground-breaking for new biologics facility J.POD® Toulouse - The manufacturing facility is expected to be operational in H2 2024 and will create upwards of 150 new high-skill jobs

Fujifilm Invests $188 Million in New Cell Culture Media Manufacturing Facility - The new facility is planned to ensure that FUJIFILM Irvine Scientific can meet increasing market demands