Plant metabolic protein tailored for nighttime growth
Everyone who took high school biology learned that photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae and select bacteria transform the Sun's energy into chemical energy during the daytime. But these photosynthetic organisms activate other biochemical pathways at night, when they generate energy by breaking down the sugars, starches, and oils that they created during the day. New work that focused on this nighttime growth found a protein that is necessary for it to occur and, surprisingly, the role of this protein was linked to the construction of the plant's cellular membranes.
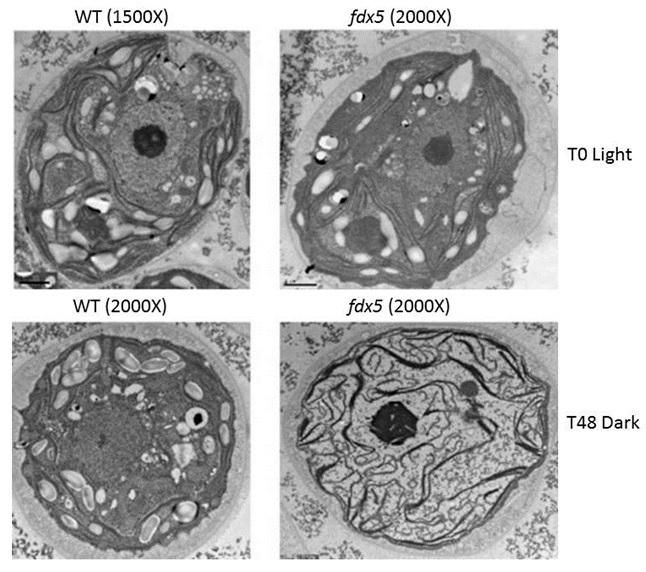
Ordinary Chlamydomonas is shown on the left and ferredoxin-5-lacking mutant Chlamydomonas on the right. Grown in the light, the mutant is fine, but grown in the dark, the cellular membrane is disorganized.
Arthur Grossman
The paper is from an integrated, international group of plant science experts, led by Carnegie's Arthur Grossman and including lead author Wenqiang Yang and co-author Martin Jonikas, both from Carnegie. It demonstrates that in the photosynthetic alga Chlamydomonas, the protein ferredoxin-5 is critical for growth in dark and for proper membrane organization.
Ferredoxin-5 is a member of a family of small iron-sulfur proteins that provide the electrons needed to drive various metabolic reactions in the cell. Photosynthetic organisms typically have multiple different types of ferredoxins, although little is known about how their functions differ.
Chlamydomonas has several ferredoxins, including the ferredoxin-5 protein described in this study. The work presented suggests that the ferredoxin variants, including ferredoxin-5, may each have specialized metabolic roles in the cell.
The team found that a specific mutant lacking the ferredoxin-5 protein was unable to grow in the dark (in the nighttime) or perform normal metabolic functions, but it had no trouble growing during the light (in the daytime).
As it turns out, the mutant alga also exhibited aberrant organization of cellular membranes when maintained in the dark, but did not exhibit them when maintained in the light.
These membranes are made up of lipids, which are fatty acids linked to a glycerol backbone. The ferredoxin-5 mutant shows marked alterations in the bond structure of many of these fatty acids, which changes the degree of saturation in the fatty acids present in the membranes. (Fully saturated fatty acids have single bonds between all of their carbon atoms while unsaturated fatty acids may have anywhere from one to several double bonds between their carbon atoms.) This, in turn, appears to impact the lipid composition of the membranes and results in aberrant membrane structure that impairs metabolic processes, including photosynthesis, that occur on those membranes.
The team's findings suggest that one of the biochemical reactions that ferredoxin-5 drives through its electron-donating abilities is this alteration in the saturation state of fatty acids. This result indicates that when the alga is in the dark, ferredoxin-5 specifically donates electrons to enzymes that specialize in desaturating fatty acids; it may also donate electrons to other processes in the dark. (In the light, however, another member of the ferredoxin family may take on this responsibility, which is why the aberrant membrane structure is only observed in plants that are maintained in darkness.) .
"This work homed in on the role of ferredoxin-5 and factors critical for photosynthetic organisms to switch between daytime and nighttime metabolism," Grossman said.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

Hahnemühle LifeScience Catalogue Industry & Laboratory by Hahnemühle
Wide variety of Filter Papers for all Laboratory and Industrial Applications
Filtration Solutions in the Life Sciences, Chemical and Pharmaceutical Sectors

Hydrosart® Ultrafilter by Sartorius
Efficient ultrafiltration for biotech and pharma
Maximum flow rates and minimum protein loss with Hydrosart® membranes

Hydrosart® Microfilter by Sartorius
Hydrophilic microfilters for bioprocesses
Minimal protein adsorption and high flow rates

Sartopore® Platinum by Sartorius
Efficient filtration with minimal protein adsorption
Reduces rinsing volume by 95 % and offers 1 m² filtration area per 10"

Polyethersulfone Ultrafilter by Sartorius
Reliable filtration with PESU membranes
Perfect for biotechnology and pharmaceuticals, withstands sterilisation and high temperatures

Polyethersulfone Microfilter by Sartorius
Biotechnological filtration made easy
Highly stable 0.1 µm PESU membranes for maximum efficiency

Sartobind® Rapid A by Sartorius
Efficient chromatography with disposable membranes
Increase productivity and reduce costs with fast cycle times

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Mechanism of dengue virus entry into cells
Quimica.ES: The New Business and Science Catalyst for Chemistry - New Spanish-language Science and Business Portal for the Chemical Industry
Potentia Pharmaceuticals Enters into Licensing and Purchase Option Agreements with Alcon

Deep-sea anglerfishes have evolved a new type of immune system - The discovery points to possible new ways of improving immune defence in patients who suffer from the consequences of a immune disabilities

Process Components Ltd - Macclesfield, United Kingdom

The scientific benefits of Rudolph's red nose
Liquid crystal liver - First and new realistic 3D model of the liver lobule since the year 1949
How cells recognize uninvited guests