Molecular characteristics of mammalian melanopsins for non-visual photoreception
Researchers at Institute for Molecular Sciences reported that a mammalian photoreceptive protein melanopsin spontaneously releases the chromophore retinal. The property would be important to regulate non-visual photoreception in mammals. This work was carried out as a collaborative work of Drs. Hisao Tsukamoto and Yuji Furutani (Institute for Molecular Science) with Yoshihiro Kubo (National Institute for Physiological Sciences), David Farrens (Oregon Health and Science University), Mitsumasa Koyanagi and Akihisa Terakita (Osaka City University).
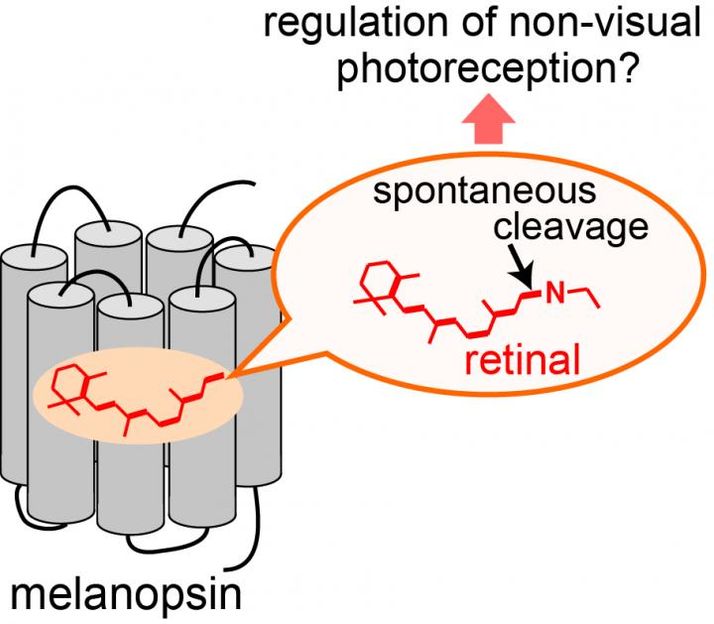
A mammalian photoreceptive protein melanopsin spontaneously releases the chromophore retinal. The property would be important to regulate non-visual photoreception in mammals.
IMS/NINS
Mammals receive light signals for not only visual but non-visual photoreception such as photoentrainment of circadian clock and pupil constriction. Previous studies have revealed that a photopigment melanopsin receives and transmits light signals in intrinsically photoreceptive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs), and the melanopsin-mediated light transmission plays an important role in non-visual photoreception of mammals. Melanopsin is a member of the opsin family, and is more closely related to photopigments in invertebrate visual cells than to pigments in vertebrate visual (rod and cone) cells. The researchers speculated that mammalian melanopsins have acquired different molecular properties from closely related invertebrate visual pigments in order to function in the non-visual photoreception. To identify such properties, they compared biochemical and spectroscopic properties of mammalian melanopsins with those of invertebrate melanopsin and visual pigment.
The researchers found that mammalian melanopsins possess a less stable bond with the chromophore retinal, a vitamin A derivative, than the closely related photopigments. This property of mammalian melanopsin would contribute to lower photosensitivity of ipRGCs to detect environmental light intensity without saturation. Furthermore, the stability of the retinal attachment is highly diversified among mammalian melanopsins, and human melanopsin possess a much weaker attachment than mouse one. Through further analyses of various primate melanopsins as well as mutagenesis analyses, the researchers showed that amino acid substitutions at particular positions are mainly responsible for the diversity of the retinal attachment stability. Comparison of amino acid residues at these positions among various mammalian melanopsins suggests that melanopsins in apes including humans have acquired and kept two residues destabilizing the bond with retinal in molecular evolution. The destabilized bond would make apes' melanopsin less photosensitive and might be important for these animals living under brighter light environment.
This study revealed that mammalian melanopsins possess characteristics suited for the non-visual photoreception, and their characteristics are diversified among mammalian species. Such insights will help us to understand non-visual photoreception in various mammals and to develop therapies and research tools using melanopsin molecules.
Original publication
Most read news
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.