Fatty liver disease and scarring have strong genetic component
Advertisement
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine say that hepatic fibrosis, which involves scarring of the liver that can result in dysfunction and, in severe cases, cirrhosis and cancer, may be as much a consequence of genetics as environmental factors.
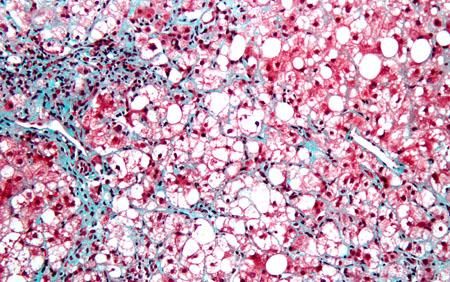
This is a micrograph of an inflamed fatty liver. White indicates areas of fat; red are hepatocytes or liver cells. Bluish areas are fibrotic strands.
Image courtesy of James Heilman, MD
"The most common known causes of hepatic fibrosis have been viral hepatitis C infections, alcohol abuse, poor diet and obesity and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis or NASH, which resembles alcoholic liver disease but occurs in people who drink little or no alcohol," said first author Rohit Loomba, MD, associate professor of clinical medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology. "We found, however, that hepatic fibrosis and steatosis (infiltration of liver cells with fat) are strong genetic traits. At around 50 percent heritability, they're more genetic than body mass index."
Loomba and colleagues performed a cross-sectional analysis of 60 pairs of twins residing in Southern California. Forty-two pairs were monozygotic or identical, meaning they developed from a single fertilized egg that split to form two embryos. Eighteen were dizygotic or fraternal, developing from two different eggs, each fertilized by separate sperm cells.
Using two advanced magnetic resonance imaging techniques that quantify fat content in the liver and liver stiffness (a measure of fibrosis), the researchers found that 26 of the 120 participants had nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which can be a precursor to development of more serious conditions. Hepatic steatosis and liver fibrosis correlated strongly with monozygotic twins, but not with dizygotic pairs.
"This evidence that hepatic steatosis and hepatic fibrosis are heritable traits has major implications," said Loomba. "It means that we can now look for the relevant genes as potential therapeutic targets."
Loomba said the research team plans to expand their research to include the role of the microbiome - the collective genomes of the microorganisms that reside within and on humans, and which also indicates a degree of heritability.
Hepatic steatosis and fibrosis are among the hottest areas in research and medicine at the moment, according to Loomba, with more than a dozen clinical trials currently underway. NAFLD, which is characterized by hepatic steatosis, is the most common cause of chronic liver disease in the United States, affecting 80 to 100 million Americans, with 18 million believed to have the more serious NASH.
Original publication
Rohit Loomba, Nicholas Schork, Chi‐Hua Chen, Ricki Bettencourt, Ana Bhatt, Brandon Ang, Phirum Nguyen, Carolyn Hernandez, Lisa Richards, Joanie Salotti, Steven Lin, Ekihiro Seki, Karen E. Nelson, Claude B. Sirlin, David Brenner; "Heritability of Hepatic Fibrosis and Steatosis Based on a Prospective Twin Study"; Gastroenterology; 2015