Exposure to phthalates could be linked to pregnancy loss
A new study of more than 300 women suggests that exposure to certain phthalates could be associated with miscarriage, mostly between 5 and 13 weeks of pregnancy. The research is the first epidemiological study on non-work-related exposure to phthalates to provide evidence for the possible link among a general population.
Out of concern over the potential health effects of phthalates, the U.S. has banned six of these substances from use in certain products made for young children. But many are still included as ingredients in paints, medical tubes, vinyl flooring, soaps, shampoos and other items. But there is little epidemiological evidence of phthalates' effects on pregnancy among women with non-occupational exposure. Jianying Hu, Huan Shen and colleagues wanted to find out if there might be a link.
The researchers tested urine samples from 132 women who had miscarriages and 172 healthy pregnant women in China. They found pregnancy loss was associated with higher levels of urinary phthalate metabolites from diethyl phthalate (DEP), di-isobutyl phthalate (DiBP) and di-n-butyl phthalate (DnBP).
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
SYGNIS AG signs supply agreement with US Biological - Agreement comprises supply of antibody labelling technology
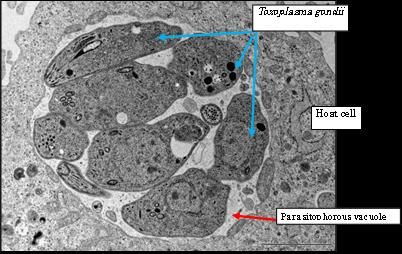
Key findings to develop a vaccine against Toxoplasma
Highly automated live cell imaging speeds up the search for new drugs
Watson Announces License Agreement With GeneraMedix for Generic Version of Ferrlecit
Risks, which get under the skin - BfR informs about health risks of tattoos and their removal
Scientists discover new option to provide bananas with resistance to dreaded Black Sigatoka disease
BUSM study reveals novel mechanism by which UVA contributes to photoaging of skin

Protein ZAP inhibits multiplication of SARS-CoV-2 by 20-fold - Silver linings in the pandemic