Estrogen worsens allergic reactions in mice
NIH study may help explain gender disparity observed in people
estradiol, a type of estrogen, enhances the levels and activity in mice of an enzyme that drives life-threatening allergic reactions, according to researchers from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The study results may help explain why women frequently experience more severe allergic reactions compared to men. Furthermore, the results reaffirm the importance of accounting for gender in the design of animal experiments.
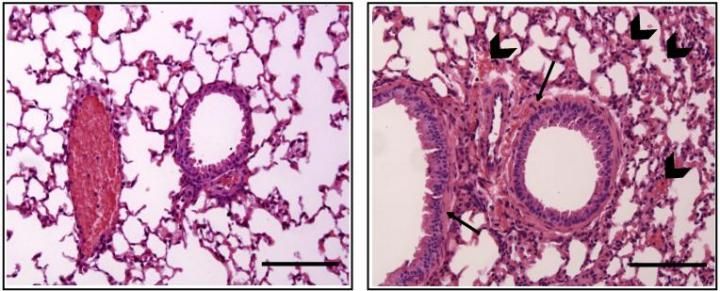
The airways of male (right) and female (left) mice respond differently to anaphylactic triggers. The female response is more severe, showing more accumulation of fluids and cells around the respiratory tract (arrows).
NIAID
Anaphylaxis is an allergic reaction triggered by food, medication or insect stings and bites. Immune cells, particularly mast cells, release enzymes that cause tissues to swell and blood vessels to widen. As a result, skin may flush or develop a rash, and in extreme cases, breathing difficulties, shock or heart attack may occur. Clinical studies have shown that women tend to experience anaphylaxis more frequently than men, but why this difference exists is unclear.
In the current study, NIAID researchers found that female mice experience more severe and longer lasting anaphylactic reactions than males. Instead of targeting immune cells, estrogen influences blood vessels, enhancing the levels and activity of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), an enzyme that causes some of the symptoms of anaphylaxis. When the researchers blocked eNOS activity, the gender disparity disappeared. In addition, giving estrogen-blocking treatments to female mice reduced the severity of their allergic responses to a level similar to those seen in males.
While the study has identified a clear role for estrogen and eNOS in driving severe anaphylactic reactions in female mice, more work is needed to see if the effects are similar in people and may be applied toward future preventive therapies.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.