Microchip reveals how tumor cells transition to invasion
Using a microengineered device that acts as an obstacle course for cells, researchers have shed new light on a cellular metamorphosis thought to play a role in tumor cell invasion throughout the body.

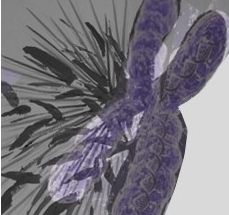
Cancer cells advance across a microchip designed to be an obstacle course for cells. The device sheds new light on how cancer cells invade and could be used to test drugs aimed at preventing cancer spread.
Ian Y. Wong / Brown University
The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a process in which epithelial cells, which tend to stick together within a tissue, change into mesenchymal cells, which can disperse and migrate individually. EMT is a beneficial process in developing embryos, allowing cells to travel throughout the embryo and establish specialized tissues. But recently it has been suggested that EMT might also play a role in cancer metastasis, allowing cancer cells to escape from tumor masses and colonize distant organs.
For this study, published in the journal Nature Materials, the researchers were able to image cancer cells that had undergone EMT as they migrated across a device that mimics the tissue surrounding a tumor.
"People are really interested in how EMT works and how it might be associated with tumor spread, but nobody has been able to see how it happens," said lead author Ian Y. Wong, assistant professor in the Brown School of Engineering and the Center for Biomedical Engineering, who performed the research as a postdoctoral fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital. "We've been able to image these cells in a biomimetic system and carefully measure how they move."
The experiments showed that the cells displayed two modes of motion. A majority plod along together in a collectively advancing group, while a few cells break off from the front, covering larger distances more quickly.
"In the context of cell migration, EMT upgrades cancer cells from an economy model to a fast sports car," Wong said. "Our technology enabled us to track the motion of thousands of 'cars' simultaneously, revealing that many sports cars get stuck in traffic jams with the economy cars, but that some sports cars break out of traffic and make their way aggressively to distant locations."
Armed with an understanding of how EMT cancer cells migrate, the researchers hope they can use this same device for preliminary testing of drugs aimed at inhibiting that migration. The work is part of a larger effort to understand the underpinnings of cancer metastasis, which is responsible for nine out of 10 cancer-related deaths.
'Obstacle course for cells'
To get this new view of how cancer cells move, the researchers borrowed microelectronics processing techniques to pattern miniaturized features on silicon wafers, which were then replicated in a rubber-like plastic called PDMS. The device consists of a small plate, about a half-millimeter square, covered in an array of microscopic pillars. The pillars, each about 10 micrometers in diameter and spaced about 10 micrometers apart, leave just enough space for the cells to weave their way through. Using microscopes and time-lapse photography, the researchers can watch cells as they travel across the plate.
"It's basically an obstacle course for cells," Wong said. "We can track individual cells, and because the size and spacing of these pillars is highly controlled, we can start to do statistical analysis and categorize these cells based on how they move."
For their experiments, the researchers started with a line of benign cancer cells that were epithelial, as identified by specific proteins they express. They then applied a chemical that induced the cells to become malignant and mesenchymal. The transition was confirmed by looking for proteins associated with the mesenchymal cell type. Once all the cells had converted, they were set free on the obstacle course.
The study showed that about 84 percent of the cells stayed together and slowly advanced across the plate. The other 16 percent sped off the front and quickly made it all the way across the device. To the researchers' surprise, they found that the cells that stayed with the group started to once again express the epithelial proteins, indicating that they had reverted back to the epithelial cell type.
"That was a remarkable result," Wong said. "Based on these results, an interesting therapeutic strategy might be to develop drugs that downgrade mesenchymal sports cars back to epithelial economy models in order to keep them stuck in traffic, rather than aggressively invading surrounding tissues."
As for the technology that made these findings possible, the researchers are hopeful that it can be used for further research and drug testing.
"We envision that this technology will be widely applicable for preclinical testing of anti-migration drugs against many different cancer cell lines or patient samples," Wong said.