New anticancer compound through accelerated drug screening process
Advertisement
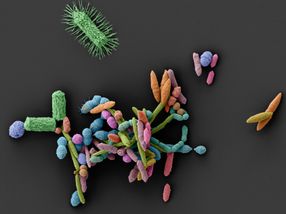
A team of research scientists from VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, the University of Turku and the University of Eastern Finland has discovered a previously unknown Cent-1 molecule that kills cancer cells. Their research also shows that new cancer drug candidates can be identified faster and at lower cost by using computer-assisted and cell-based screening of compounds.
The objective of the research project led by Marko Kallio, Principal Scientist at VTT, was to accelerate the drug development process by identifying new compounds that would possess similar binding properties and cellular phenotype , but a different chemical structure, as the selected drugs in clinical use or investigational compounds in development.
The scientists combined computer-based screening and cell-based assays to create a method that can significantly accelerate drug discovery and thereby lower development costs. It is highly likely that the new compounds identified using this method have not yet been patented.
The research team conducted a computer-assisted screening of 65,000 compounds and cell-based assays on the 150 highest scoring hit compounds, before identifying the Cent-1 molecule. The Cent-1 molecule kills cancer cells through a mechanism similar to that of the template drug Rigosertib that is currently under commercial development. However, since the chemical structure of the Cent-1 compound differs from Rigosertib, there are no major obstacles to further development.
What makes the study also significant is evidence that Rigosertib did not inhibit its reported target genes; there is reason to believe that the drug has a different mechanism of action at molecular level than anticipated. This drug discovery related study was published in Molecular Cancer Therapeutics.
Most read news
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.