Movies synchronize brains
When we watch a movie, our brains react to it immediately in a way similar to other people's brains.
Advertisement
Researchers at Aalto University in Finland have succeeded in developing a method fast enough to observe immediate changes in the function of the brain even when watching a movie. By employing movies it was possible to investigate the function of the human brain in experimental conditions that are close to natural. Traditionally, in neuroscience research, simple stimuli, such as checkerboard patterns or single images, have been used.
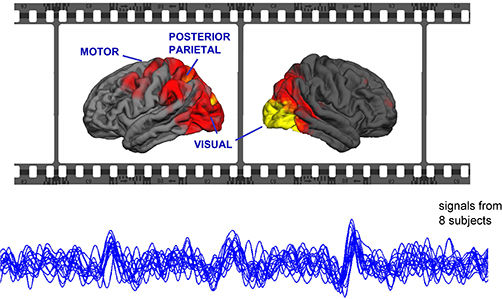
The study found a notable correlation between the brain signals created by films in all test participants (below), and these similar signals were found in specific areas of the brain (above). The image is an example of signal components at a frequency of 1-5 Hz.
Aalto University
Viewing a movie creates multilevel changes in the brain function. Despite the complexity of the stimulus, the elicited brain activity patterns show remarkable similarities across different people – even at the time scale of fractions of seconds.
"The analysis revealed important similarities between brain signals of different people during movie viewing. These similar kinds or synchronized signals were found in brain areas that are connected with the early-stage processing of visual stimuli, detection of movement and persons, motor coordination and cognitive functions. The results imply that the contents of the movie affected certain brain functions of the subjects in a similar manner", explains Kaisu Lankinen the findings of her doctoral research.
So far, studies in this field have mainly been based on functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). However, given the superior temporal resolution, within milliseconds, magnetoencephalography (MEG) is able to provide more complete picture of the fast brain processes. With the help of MEG and new analysis methods, investigation of significantly faster brain processes is possible and it enables detection of brain activity in frequencies higher than before.
In the novel analysis, brain imaging was combined with machine-learning methodology, with which signals of a similar form were mined from the brain data.
The research result was recently published in the NeuroImage journal.