Molecular nano-spies to make light work of disease detection
A world of cloak-and-dagger pharmaceuticals has come a step closer with the development of stealth compounds programmed to spring into action when they receive the signal.
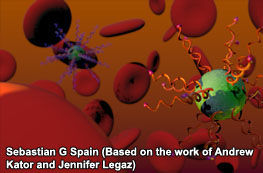
Cartoon of DNA-containing molecular hybrids in the presence of red blood cells. (Note: cells and DNA-hybrids are shown in a stylised schematic form and are not to scale)
University of Nottingham
Researchers at the University of Nottingham’s School of Pharmacy have designed and tested large molecular complexes that will reveal their true identity only when they’ve reached their intended target, like disguised saboteurs working deep behind enemy lines.
The compounds have been developed as part of a five-year programme funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) called “Bar-Coded Materials”.
The cloak each spherical complex wears is perhaps more a plastic mac: a sheath of biocompatible polymer that encapsulates and shrouds biologically active material inside, preventing any biological interaction so long as the shield remains in place.
The smart aspect is in the DNA-based zips that hold the coat in place until triggered to undo. Because any DNA code (or “molecular cipher”) can be chosen, the release mechanism can be bar-coded so that it is triggered by a specific biomarker – for example a message from a disease gene.
What is then exposed – an active pharmaceutical compound, a molecular tag to attach to diseased tissue, or a molecular beacon to signal activation – depends on what function is needed.
Professor Cameron Alexander, who leads the project, says: “These types of switchable nanoparticles could be extremely versatile. As well as initial detection of a medical condition, they could be used to monitor the progress of diseases and courses of treatment, or adapted to deliver potent drugs at particular locations in a patient’s body. It might even become possible to use mobile phones rather than medical scanners to detect programmed responses from later generations of the devices.”
In their initial trials, the team has proved the concept works in the test tube – the switchable molecular constructs do respond as expected when presented with the right molecular signals. The group is now working hard to push their idea forwards.
An early application might be in dipstick technology – testing for specific infections in a blood or spit sample, for example. But because the polymer coating (called polyethylene glycol) is biocompatible, the researchers are hopeful that in the long run “self-authenticating medicines” based on the approach could be injected into patients, to seek out diseased tissue, and report their success.
“The key to this breakthrough has been the five-year EPSRC Leadership Fellowship awarded to me back in 2009”, Professor Alexander comments. “This has provided the stability of funding to recruit and retain an outstanding team, who have been integral to realising the ideas put forward in the Fellowship. It has also given us the freedom to explore a whole range of new concepts, as well as the time needed to test our ideas to bring this and other breakthroughs within reach”.