Mitochondria Separate Their Waste
Freiburg researcher shows that cellular power plants collect and break down damaged molecules
In order to protect themselves from harmful substances, cells need to keep the mitochondria – the boiler room, so to speak – shipshape. Up to now, it was unclear whether this housekeeping work involves sorting out defective proteins when they digest mitochondria. Dr. Joern Dengjel from the Center for Biological Systems Analysis (ZBSA), Freiburg Institute for Advanced Studies (FRIAS), and the Cluster of Excellence BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies of the University of Freiburg has now discovered in collaboration with researchers from the Hebrew University in Jerusalem, Israel, that the proteins are sorted out during the constant fusion and fission of mitochondria. The team published their findings in the journal Nature Communications.
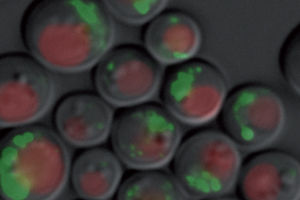
Yeast cells digest their mitochondria in long-time cultures. This process is called mitophagy. Proteins that are digested at a different speed are marked with a fluorescent dye.
© Jörn Dengjel
The process of mitophagy, in which tiny digestive bubbles surround the mitochondria, serves to recycle waste for the cell. Damaged proteins can no longer carry out their function correctly and need to be broken down. Errors in the digestion of mitochondria appear in old age and in the case of neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. A better understanding of mitophagy could be the key to counteracting the faulty degradation of cellular components, potentially enabling researchers to develop new therapies for neurodegenerative diseases.
In contrast to bacteria, yeast cells posses mitochondria and are also easy to grow in the laboratory. The researchers used yeasts to observe the processes of mitophagy. Dr. Hagai Abeliovich from the Hebrew University developed a new method for making yeast cells digest mitochondria. Currently, researchers accomplish this by placing stress on the cells with chemicals. With the new method, yeast cells in long-term cultures begin digesting mitochondria of their own accord – as soon as they have used up all available nutrients. During mitophagy Dengjel succeeded in measuring whether all proteins inside the mitochondria were broken down at the same speed. Indeed, the cell broke down some proteins more quickly than others. When he observed the cells under a fluorescence microscope, he ascertained that the marked proteins in the mitochondria also behaved differently. They appear to be sorted.
The rules by which the sorting is carried out are as yet unknown. However, the researchers demonstrated that mitochondrial dynamics are involved: Mitochondria fuse and divide constantly, forming a network in the process. Genetically modified yeasts that lack these dynamics but form small, round mitochondria exhibit no sorting of the proteins. “The damaged proteins are sorted slowly into an area of the network with each fusion and fission. This mitochondrion is marked and broken down,” says Dengjel. In other words, mitophagy plays the role of garbage collector, separating and recycling waste for the cell. Now Dengjel wants to find out what characterizes the proteins that are sorted out.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Fluorescence microscopy
Fluorescence microscopy has revolutionized life sciences, biotechnology and pharmaceuticals. With its ability to visualize specific molecules and structures in cells and tissues through fluorescent markers, it offers unique insights at the molecular and cellular level. With its high sensitivity and resolution, fluorescence microscopy facilitates the understanding of complex biological processes and drives innovation in therapy and diagnostics.

Topic world Fluorescence microscopy
Fluorescence microscopy has revolutionized life sciences, biotechnology and pharmaceuticals. With its ability to visualize specific molecules and structures in cells and tissues through fluorescent markers, it offers unique insights at the molecular and cellular level. With its high sensitivity and resolution, fluorescence microscopy facilitates the understanding of complex biological processes and drives innovation in therapy and diagnostics.