Dirty job made easier
Microfluidic technique recovers DNA for IDs
A team of researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and Applied Research Associates, Inc. (ARA, Alexandria, Va.) has demonstrated an improved microfluidic technique for recovering DNA from real-world, complex mixtures such as dirt. Their technique delivers DNA from these crude samples with much less effort and in less time than conventional techniques. It yields DNA concentrations that are optimal for human identification procedures and can potentially be miniaturized for use outside the laboratory.
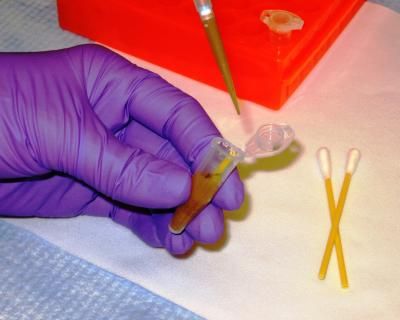
A laboratory technician pipettes dirt dissolved in a buffer solution from which DNA will be recovered using a novel NIST/Applied Research Associates microfluidic extraction technique. The dirt, originally collected on a swab (lower section seen in vial) like those on the right, is an example of a crude sample from which DNA for human identification has typically been difficult to obtain.
Michael E. Newman, NIST
Forensic DNA testing is extensively used to link individuals to crimes, establish paternity, solve missing person cases, identify casualties in military and mass fatality events, and provide genealogical histories. Typically, it takes a skilled technician in a properly equipped laboratory 1-2 days to extract DNA from a sample, quantify the amount, make multiple copies of specific genetic sequences (PCR amplification), and then create a "DNA signature" that is unique to an individual. However, when crude samples are the source of the desired DNA, the contaminants and particulates mixed in with the genetic material can seriously complicate the reading of a complete and accurate DNA signature. The additional purification steps needed for conventional means of handling crude samples, such as filtering, not only lengthen the processing time but also tend to reduce the quantity and concentration of DNA delivered—making human identification more difficult or impossible.
The new NIST/ARA technique is based on one the team first developed four years ago for crude samples called "gradient elution moving boundary electrophoreses" or GEMBE. GEMBE separates specific components of a sample by a molecular "tug-of-war." The sample is pushed in one direction by an electric field and in the other by the counterflow of a buffer solution. Gradually reducing the buffer flow allows selected components from the sample to pass into a microfluidic channel to be analyzed. Unwanted components of the crude sample are kept out.
To work with DNA, the researchers modified GEMBE so that two different buffer solutions—one with ions that move quickly and one with ions that move slowly during electrophoresis—are placed in the separate reservoirs connected by the microchannel. When a crude sample is suspended in the slow ion solution and electric current is applied, the DNA within the sample moves into the microchannel and concentrates at the interface between the two buffers. Unwanted contaminants and particulates—including those that can inhibit PCR amplification—are left behind. The collected DNA can be quantified directly in the microchannel and then delivered into a vial for further processing.
To demonstrate the forensic capabilities of its new technique, the NIST/ARA team extracted, purified, quantified and concentrated human genomic DNA from both clean and dirty buccal (cheek cell) swabs. In both cases, the process yielded full DNA signatures.
Original publication
Most read news
Original publication
E.A. Strychalski, C. Konek, E.L.R. Butts, P.M. Vallone, A.C. Henry and D. Ross. DNA purification from crude samples for human identification using gradient elution isotachophoresis. Electrophoresis, Vol. 34, No.17, pp. 2522. Published online Sept. 2, 2013.
Organizations
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you
LowCross-Buffer® by CANDOR Bioscience
Improve Accuracy of Your ELISAs!
LowCross-Buffer

Liquid Plate Sealer by CANDOR Bioscience
Protection for Antibodies and Antigens Coated on Plates
For Long-Term Stability of Antibodies Coated on ELISA-Plates, Affinity Columns and Other Surfaces

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.




















































