New allosteric inhibitors of cholesterol synthesis – an alternative to statins?
Researchers in Israel have identified a new catalytic anti-oxidant that could be a promising alternative to statins – the most prescribed cholesterol-lowering drugs in the world.
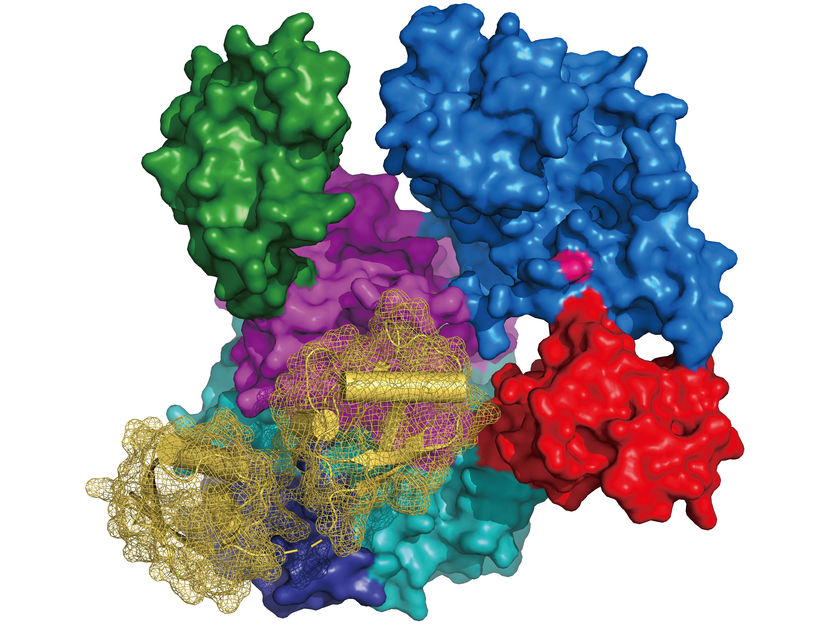
Statins reduce cholesterol levels in the body by acting as competitive inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) reductase – the enzyme that catalyses cholesterol biosynthesis. But some patients don’t respond to statins and catalytic anti-oxidants have an advantage over statins: in their dual mode of action, they also reduce free radicals in the body.
The scientists showed that the catalytic antioxidant, Fe-1, and its analogues, inhibit HMG-CoA reductase in a different way to statins. They propose that the amphipolar nature of the drug macrocycles is important for binding to an allosteric site of HMG-coA reductase and inhibiting the enzyme’s catalytic activity.
Most read news
Original publication
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Cavernous_sinus_thrombosis
S._Robert_Rozbruch
Silent_Holocaust